Filter News
Area of Research
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Coronavirus (28)
- (-) Microscopy (31)
- (-) Polymers (17)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (66)
- Advanced Reactors (21)
- Artificial Intelligence (58)
- Big Data (36)
- Bioenergy (64)
- Biology (74)
- Biomedical (39)
- Biotechnology (13)
- Buildings (35)
- Chemical Sciences (29)
- Clean Water (27)
- Climate Change (68)
- Composites (15)
- Computer Science (119)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (17)
- Decarbonization (51)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (59)
- Environment (143)
- Exascale Computing (25)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (24)
- Fusion (37)
- Grid (43)
- High-Performance Computing (53)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (30)
- ITER (5)
- Machine Learning (31)
- Materials (75)
- Materials Science (75)
- Mathematics (6)
- Mercury (10)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Molten Salt (6)
- Nanotechnology (28)
- National Security (36)
- Net Zero (9)
- Neutron Science (73)
- Nuclear Energy (70)
- Partnerships (15)
- Physics (30)
- Quantum Computing (22)
- Quantum Science (38)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (11)
- Simulation (35)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (22)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (36)
- Sustainable Energy (87)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (62)
Media Contacts

Researchers at ORNL and the University of Maine have designed and 3D-printed a single-piece, recyclable natural-material floor panel tested to be strong enough to replace construction materials like steel.
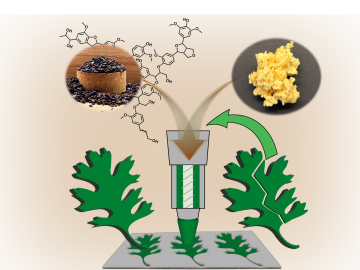
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists ingeniously created a sustainable, soft material by combining rubber with woody reinforcements and incorporating “smart” linkages between the components that unlock on demand.

Researchers set a new benchmark for future experiments making materials in space rather than for space. They discovered that many kinds of glass have similar atomic structure and arrangements and can successfully be made in space. Scientists from nine institutions in government, academia and industry participated in this 5-year study.

New computational framework speeds discovery of fungal metabolites, key to plant health and used in drug therapies and for other uses.

Speakers, scientific workshops, speed networking, a student poster showcase and more energized the Annual User Meeting of the Department of Energy’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, or CNMS, Aug. 7-10, near Market Square in downtown Knoxville, Tennessee.

Madhavi Martin brings a physicist’s tools and perspective to biological and environmental research at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, supporting advances in bioenergy, soil carbon storage and environmental monitoring, and even helping solve a murder mystery.

When reading the novel Jurassic Park as a teenager, Jerry Parks found the passages about gene sequencing and supercomputers fascinating, but never imagined he might someday pursue such futuristic-sounding science.

Nature-based solutions are an effective tool to combat climate change triggered by rising carbon emissions, whether it’s by clearing the skies with bio-based aviation fuels or boosting natural carbon sinks.

Tomonori Saito, a distinguished innovator in the field of polymer science and senior R&D staff member at ORNL, was honored on May 11 in Columbus, Ohio, at Battelle’s Celebration of Solvers.
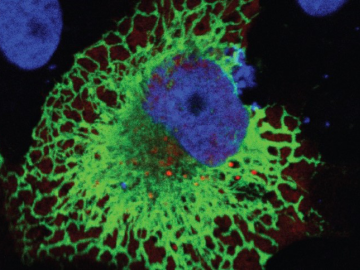
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists exploring bioenergy plant genetics have made a surprising discovery: a protein domain that could lead to new COVID-19 treatments.




