Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (122)
- (-) Renewable Energy (2)
- (-) Supercomputing (153)
- Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (102)
- Biology and Soft Matter (4)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Chemical and Engineering Materials (3)
- Chemistry and Physics at Interfaces (7)
- Clean Energy (168)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (7)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Chemistry (5)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Data (1)
- Earth Sciences (1)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (7)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (2)
- Functional Materials for Energy (8)
- Fusion and Fission (32)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Geographic Information Science and Technology (1)
- Isotopes (21)
- Materials for Computing (13)
- Materials Synthesis from Atoms to Systems (8)
- Materials Under Extremes (7)
- National Security (45)
- Neutron Data Analysis and Visualization (2)
- Neutron Science (72)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (27)
- Quantum Condensed Matter (3)
- Quantum information Science (4)
- Sensors and Controls (2)
- Transportation Systems (4)
News Type
News Topics
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Advanced Reactors (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (21)
- Big Data (13)
- Bioenergy (5)
- Biology (6)
- Biomedical (8)
- Biotechnology (1)
- Buildings (3)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Clean Water (2)
- Climate Change (12)
- Composites (2)
- Computer Science (47)
- Coronavirus (7)
- Cybersecurity (2)
- Decarbonization (4)
- Energy Storage (7)
- Environment (18)
- Exascale Computing (12)
- Frontier (13)
- Fusion (2)
- Grid (3)
- High-Performance Computing (20)
- Isotopes (6)
- Machine Learning (7)
- Materials (21)
- Materials Science (20)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (7)
- Nanotechnology (9)
- National Security (3)
- Net Zero (1)
- Neutron Science (14)
- Nuclear Energy (11)
- Partnerships (3)
- Physics (13)
- Polymers (4)
- Quantum Computing (11)
- Quantum Science (10)
- Security (2)
- Simulation (10)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (2)
- Summit (21)
- Sustainable Energy (5)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (7)
Media Contacts
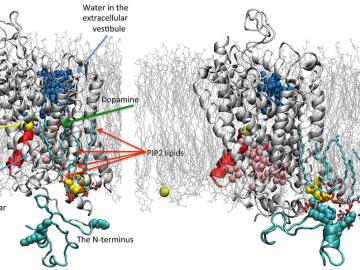
In an era of instant communication, perhaps no message-passing system is more underappreciated than the human body. Underlying each movement, each mood, each sight, sound, or smell, an army of specialized cells called neurons relays signals that register in the brain and connect us to our environment.
In the United States, the use of natural gas for electricity generation continues to grow. The driving forces behind this development? A boom in domestic natural gas production, historically low prices, and increased scrutiny over fossil fuels’ carbon emissions. Though coal still acco...
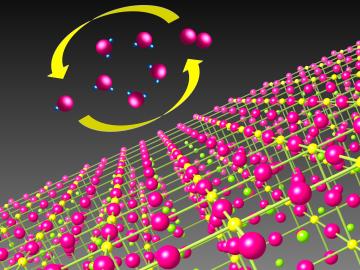
Catalysts make chemical reactions more likely to occur. In most cases, a catalyst that’s good at driving chemical reactions in one direction is bad at driving reactions in the opposite direction. However, a research team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory ...
![In unbound calyx[4]pyrrole, two pyrrole “petals” are flipped up and two, down. In unbound calyx[4]pyrrole, two pyrrole “petals” are flipped up and two, down.](/sites/default/files/styles/list_page_thumbnail/public/news/images/anion_hr5_0.jpg?itok=sGtLzH0E)
Atomic charges in chemical solutions are like Switzerland—they strive for neutrality. The tendency to balance charges drives dynamics when charged atoms or molecules, called ions, are present in solutions. Recently, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laborat...

Rare earth elements are metals used in technologies from wind turbines and magnetic resonance imaging agents to industrial catalysts and high-definition televisions. Most are lanthanides, elements with atomic number from 57 to 71, lanthanum to lutetium, in the periodic table. The la...

Nearly 100 commercial nuclear reactors supply one-fifth of America’s energy. For each fuel rod in a reactor assembly, only 5 percent of its energy is consumed before fission can no longer be sustained efficiently for power production and the fuel assembly must be replaced. Power plan...