Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (122)
- (-) Quantum information Science (4)
- Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (102)
- Biology and Soft Matter (4)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Chemical and Engineering Materials (3)
- Chemistry and Physics at Interfaces (7)
- Clean Energy (168)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (7)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Chemistry (5)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Data (1)
- Earth Sciences (1)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (7)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (2)
- Functional Materials for Energy (8)
- Fusion and Fission (32)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Geographic Information Science and Technology (1)
- Isotopes (21)
- Materials for Computing (13)
- Materials Synthesis from Atoms to Systems (8)
- Materials Under Extremes (7)
- National Security (45)
- Neutron Data Analysis and Visualization (2)
- Neutron Science (72)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (27)
- Quantum Condensed Matter (3)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Sensors and Controls (2)
- Supercomputing (153)
- Transportation Systems (4)
News Type
News Topics
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Advanced Reactors (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (4)
- Big Data (2)
- Bioenergy (3)
- Biomedical (2)
- Buildings (1)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Clean Water (2)
- Composites (2)
- Computer Science (9)
- Coronavirus (1)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Decarbonization (1)
- Energy Storage (6)
- Environment (6)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fusion (2)
- Grid (2)
- High-Performance Computing (1)
- Isotopes (6)
- Machine Learning (2)
- Materials (19)
- Materials Science (17)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (8)
- Nanotechnology (9)
- Neutron Science (9)
- Nuclear Energy (9)
- Partnerships (3)
- Physics (11)
- Polymers (4)
- Quantum Computing (1)
- Quantum Science (4)
- Security (1)
- Space Exploration (1)
- Summit (1)
- Sustainable Energy (3)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (4)
Media Contacts
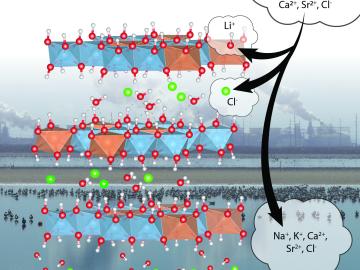
In the quest for domestic sources of lithium to meet growing demand for battery production, scientists at ORNL are advancing a sorbent that can be used to more efficiently recover the material from brine wastes at geothermal power plants.
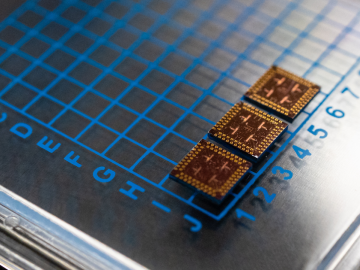
Scientists at have experimentally demonstrated a novel cryogenic, or low temperature, memory cell circuit design based on coupled arrays of Josephson junctions, a technology that may be faster and more energy efficient than existing memory devices.

Eugene P. Wigner Fellow Victor Fung’s story is proof that a series of positive experiences around science and happy accidents can lead to a rewarding research career. He joined ORNL in 2019.
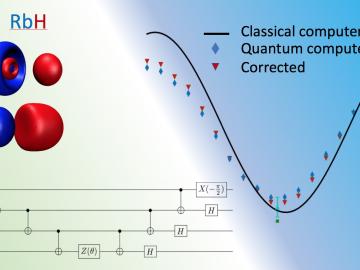
Researchers at ORNL have developed a quantum chemistry simulation benchmark to evaluate the performance of quantum devices and guide the development of applications for future quantum computers.

Friederike Bock, a Eugene P. Wigner Fellow, wants everyone to know scientists aren’t just robots—they want to help others understand their research, and they have wide-ranging interests.

Students often participate in internships and receive formal training in their chosen career fields during college, but some pursue professional development opportunities even earlier.
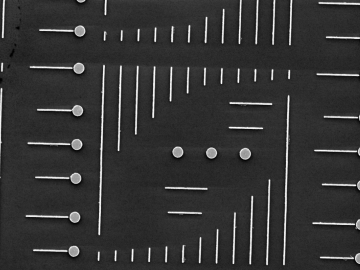
Electrons in atoms are pretty talented. They can form chemical bonds, get kicked out of the atom and even “jump” to different locations based on their energetic states.

A modern, healthy transportation system is vital to the nation’s economic security and the American standard of living. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is engaged in a broad portfolio of scientific research for improved mobility

Six new nuclear reactor technologies are set to deploy for commercial use between 2030 and 2040. Called Generation IV nuclear reactors, they will operate with improved performance at dramatically higher temperatures than today’s reactors.

Rare earth elements are the “secret sauce” of numerous advanced materials for energy, transportation, defense and communications applications.


