Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Biology (60)
- (-) Chemical Sciences (25)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (41)
- Advanced Reactors (8)
- Artificial Intelligence (48)
- Big Data (26)
- Bioenergy (51)
- Biomedical (29)
- Biotechnology (11)
- Buildings (19)
- Clean Water (14)
- Climate Change (50)
- Composites (8)
- Computer Science (86)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (46)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (29)
- Environment (104)
- Exascale Computing (26)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (24)
- Fusion (31)
- Grid (25)
- High-Performance Computing (44)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (27)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (22)
- Materials (43)
- Materials Science (45)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (7)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (16)
- National Security (39)
- Net Zero (8)
- Neutron Science (47)
- Nuclear Energy (55)
- Partnerships (18)
- Physics (29)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (21)
- Quantum Science (30)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (11)
- Simulation (32)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (12)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (30)
- Sustainable Energy (47)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts

A team of federal contractor and national laboratory engineers and scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management has been nationally distinguished as “Heroes of Chemistry” for making the world better through their effort, ingenuity, creativity and perseverance.

Brian Sanders is focused on impactful, multidisciplinary science at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, developing solutions for everything from improved imaging of plant-microbe interactions that influence ecosystem health to advancing new treatments for cancer and viral infections.

ORNL's Guang Yang and Andrew Westover have been selected to join the first cohort of DOE’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy Inspiring Generations of New Innovators to Impact Technologies in Energy 2024 program. The program supports early career scientists and engineers in their work to convert disruptive ideas into impactful energy technologies.

When Oak Ridge National Laboratory's science mission takes staff off-campus, the lab’s safety principles follow. That’s true even in the high mountain passes of Washington and Oregon, where ORNL scientists are tracking a tree species — and where wildfires have become more frequent and widespread.

Early career scientist Frankie White's was part of two major isotope projects at the same time he was preparing to be a father. As co-lead on a team that achieved the first synthesis and characterization of a radium compound using single crystal X-ray diffraction and part of a team that characterized the properties of promethium, White reflects on the life-changing timeline at work, and at home.

John Lagergren, a staff scientist in Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Plant Systems Biology group, is using his expertise in applied math and machine learning to develop neural networks to quickly analyze the vast amounts of data on plant traits amassed at ORNL’s Advanced Plant Phenotyping Laboratory.

The BIO-SANS instrument, located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s High Flux Isotope Reactor, is the latest neutron scattering instrument to be retrofitted with state-of-the-art robotics and custom software. The sophisticated upgrade quadruples the number of samples the instrument can measure automatically and significantly reduces the need for human assistance.

Plans to unite the capabilities of two cutting-edge technological facilities funded by the Department of Energy’s Office of Science promise to usher in a new era of dynamic structural biology. Through DOE’s Integrated Research Infrastructure, or IRI, initiative, the facilities will complement each other’s technologies in the pursuit of science despite being nearly 2,500 miles apart.
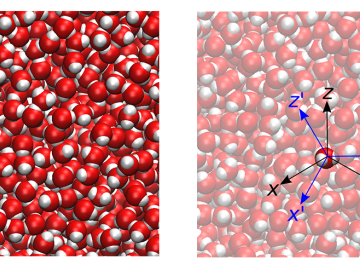
Computational scientists at ORNL have published a study that questions a long-accepted factor in simulating the molecular dynamics of water: the 2 femtosecond time step. According to the team’s findings, using anything greater than a 0.5 femtosecond time step can introduce errors in both the dynamics and thermodynamics when simulating water using a rigid-body description.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed lubricant additives that protect both water turbine equipment and the surrounding environment.


