Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Biology and Environment (25)
- (-) Computer Science (3)
- (-) Fusion Energy (5)
- (-) Materials (38)
- (-) Quantum information Science (5)
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Clean Energy (50)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Fusion and Fission (27)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- National Security (33)
- Neutron Science (13)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (23)
- Supercomputing (58)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (3)
- (-) Clean Water (10)
- (-) Composites (7)
- (-) Cybersecurity (6)
- (-) Exascale Computing (6)
- (-) Grid (5)
- (-) Machine Learning (10)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (15)
- (-) Quantum Science (16)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (20)
- Artificial Intelligence (14)
- Big Data (9)
- Bioenergy (42)
- Biology (59)
- Biomedical (16)
- Biotechnology (11)
- Buildings (3)
- Chemical Sciences (30)
- Climate Change (33)
- Computer Science (35)
- Coronavirus (12)
- Critical Materials (8)
- Decarbonization (21)
- Energy Storage (28)
- Environment (79)
- Frontier (5)
- Fusion (10)
- High-Performance Computing (20)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (11)
- ITER (1)
- Materials (61)
- Materials Science (56)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (6)
- Microscopy (27)
- Molten Salt (2)
- Nanotechnology (33)
- National Security (5)
- Net Zero (3)
- Neutron Science (30)
- Partnerships (12)
- Physics (26)
- Polymers (11)
- Quantum Computing (2)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (3)
- Simulation (13)
- Space Exploration (1)
- Summit (11)
- Sustainable Energy (30)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (8)
Media Contacts
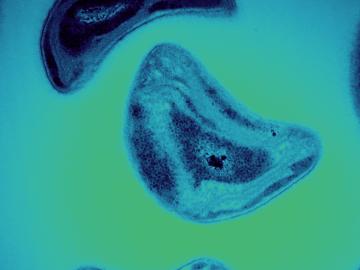
A team led by ORNL and the University of Michigan have discovered that certain bacteria can steal an essential compound from other microbes to break down methane and toxic methylmercury in the environment.

Of the $61 million recently announced by the U.S. Department of Energy for quantum information science studies, $17.5 million will fund research at DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. These projects will help build the foundation for the quantum internet, advance quantum entanglement capabilities — which involve sharing information through paired particles of light called photons — and develop next-generation quantum sensors.
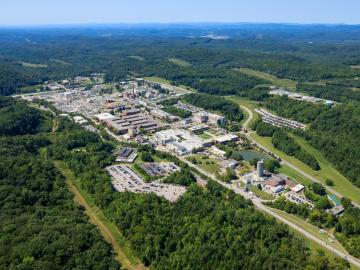
Anyone familiar with ORNL knows it’s a hub for world-class science. The nearly 33,000-acre space surrounding the lab is less known, but also unique.

Moving to landlocked Tennessee isn’t an obvious choice for most scientists with new doctorate degrees in coastal oceanography.

As rising global temperatures alter ecosystems worldwide, the need to accurately simulate complex environmental processes under evolving conditions is more urgent than ever.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory expertise in fission and fusion has come together to form a new collaboration, the Fusion Energy Reactor Models Integrator, or FERMI

Sergei Kalinin, a scientist and inventor at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elected a fellow of the Microscopy Society of America professional society.
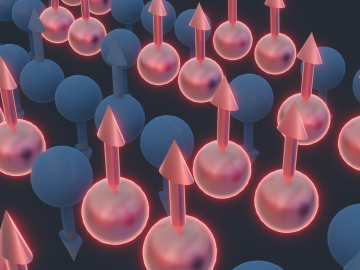
Using complementary computing calculations and neutron scattering techniques, researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories and the University of California, Berkeley, discovered the existence of an elusive type of spin dynamics in a quantum mechanical system.
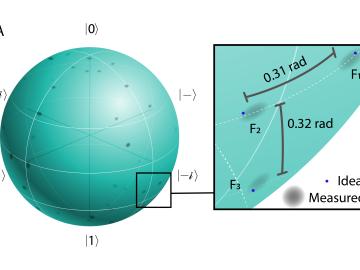
A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Purdue University has taken an important step toward this goal by harnessing the frequency, or color, of light. Such capabilities could contribute to more practical and large-scale quantum networks exponentially more powerful and secure than the classical networks we have today.

Six scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory were named Battelle Distinguished Inventors, in recognition of obtaining 14 or more patents during their careers at the lab.


