Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (54)
- Clean Energy (61)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Fusion and Fission (29)
- Fusion Energy (5)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (7)
- Materials (70)
- Materials for Computing (9)
- National Security (21)
- Neutron Science (28)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (26)
- Quantum information Science (5)
- Supercomputing (62)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Big Data (30)
- (-) Biomedical (45)
- (-) Composites (15)
- (-) Machine Learning (35)
- (-) Mercury (9)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (80)
- (-) Physics (52)
- (-) Polymers (20)
- (-) Quantum Science (56)
- (-) Sustainable Energy (74)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (81)
- Advanced Reactors (18)
- Artificial Intelligence (75)
- Bioenergy (74)
- Biology (80)
- Biotechnology (18)
- Buildings (31)
- Chemical Sciences (51)
- Clean Water (15)
- Climate Change (70)
- Computer Science (139)
- Coronavirus (34)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (31)
- Decarbonization (64)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (69)
- Environment (137)
- Exascale Computing (34)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Frontier (38)
- Fusion (43)
- Grid (38)
- High-Performance Computing (69)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (45)
- ITER (4)
- Materials (100)
- Materials Science (94)
- Mathematics (6)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (36)
- Molten Salt (3)
- Nanotechnology (42)
- National Security (53)
- Net Zero (11)
- Neutron Science (96)
- Partnerships (43)
- Quantum Computing (29)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (22)
- Simulation (38)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (15)
- Statistics (2)
- Summit (50)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (52)
Media Contacts
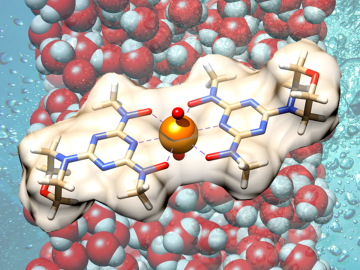
Sometimes solutions to the biggest problems can be found in the smallest details. The work of biochemist Alex Johs at Oak Ridge National Laboratory bears this out, as he focuses on understanding protein structures and molecular interactions to resolve complex global problems like the spread of mercury pollution in waterways and the food supply.
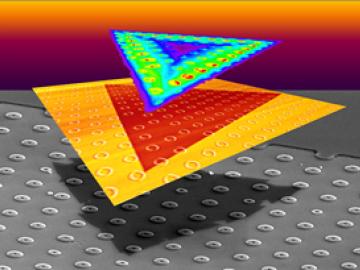
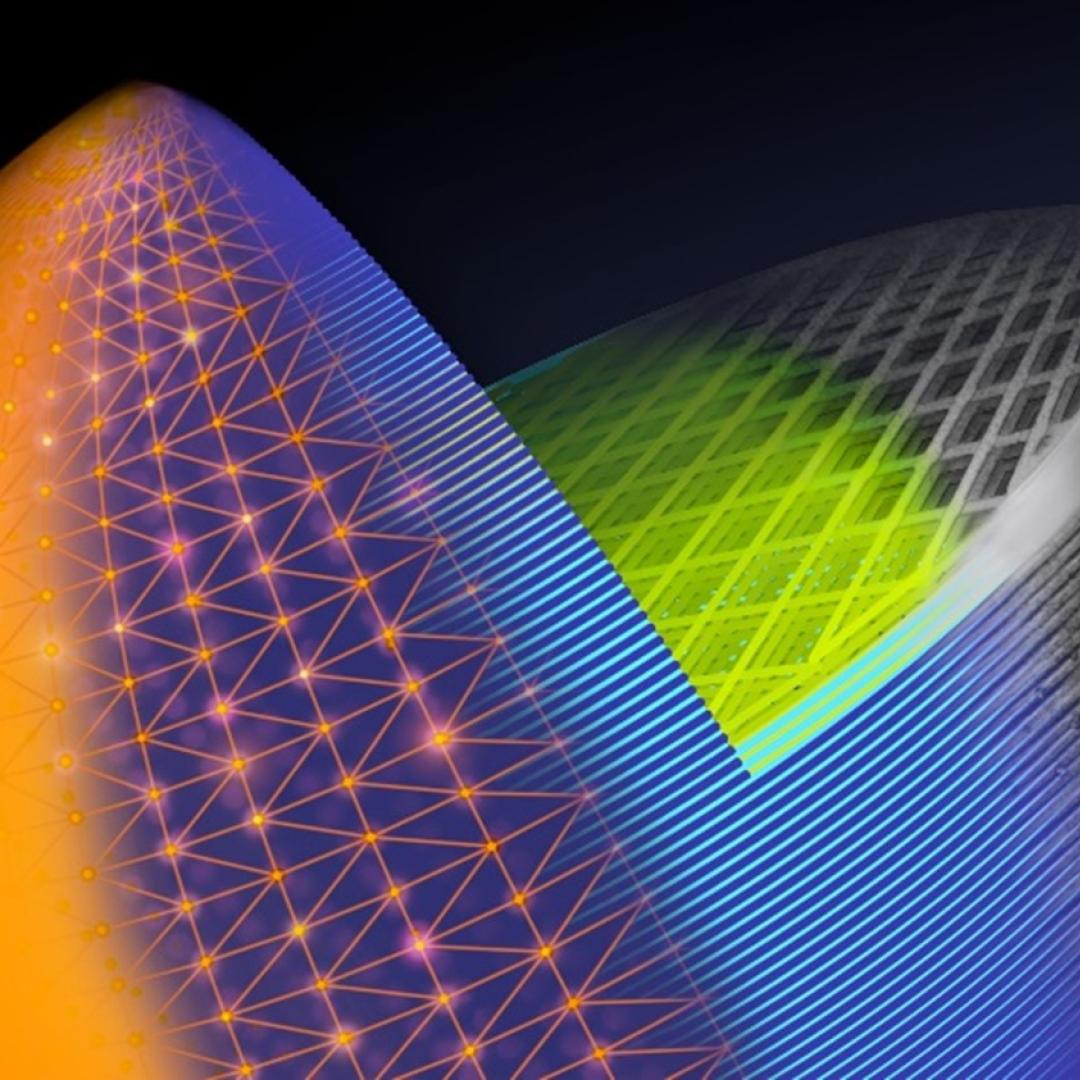
A team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory explored how atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) crystals can grow over 3D objects and how the curvature of those objects can stretch and strain the

An ORNL-led team's observation of certain crystalline ice phases challenges accepted theories about super-cooled water and non-crystalline ice. Their findings, reported in the journal Nature, will also lead to better understanding of ice and its various phases found on other planets, moons and elsewhere in space.
Scientists have demonstrated a new bio-inspired material for an eco-friendly and cost-effective approach to recovering uranium from seawater.

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., May 7, 2019—Energy Secretary Rick Perry, Congressman Chuck Fleischmann and lab officials today broke ground on a multipurpose research facility that will provide state-of-the-art laboratory space

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and Washington State University teamed up to investigate the complex dynamics of low-water liquids that challenge nuclear waste processing at federal cleanup sites.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are working to understand both the complex nature of uranium and the various oxide forms it can take during processing steps that might occur throughout the nuclear fuel cycle.
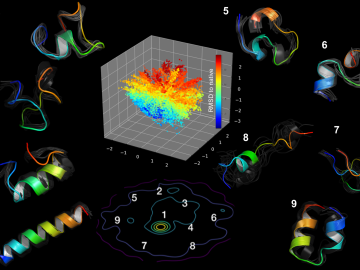
Using artificial neural networks designed to emulate the inner workings of the human brain, deep-learning algorithms deftly peruse and analyze large quantities of data. Applying this technique to science problems can help unearth historically elusive solutions.
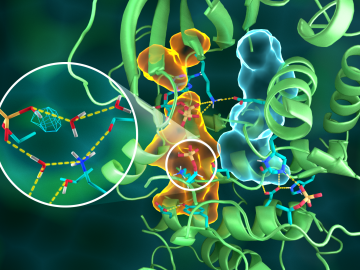
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., March 20, 2019—Direct observations of the structure and catalytic mechanism of a prototypical kinase enzyme—protein kinase A or PKA—will provide researchers and drug developers with significantly enhanced abilities to understand and treat fatal diseases and neurological disorders such as cancer, diabetes, and cystic fibrosis.

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., March 11, 2019—An international collaboration including scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory solved a 50-year-old puzzle that explains why beta decays of atomic nuclei


