Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (30)
- Clean Energy (56)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (5)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (2)
- Fusion and Fission (11)
- Fusion Energy (8)
- Isotopes (8)
- Materials (28)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (9)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (9)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Supercomputing (17)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (18)
- (-) Biomedical (15)
- (-) Energy Storage (48)
- (-) Environment (58)
- (-) Fusion (17)
- (-) Isotopes (14)
- (-) Machine Learning (13)
- (-) Space Exploration (11)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (50)
- Artificial Intelligence (21)
- Big Data (21)
- Bioenergy (22)
- Biology (25)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (25)
- Chemical Sciences (24)
- Clean Water (13)
- Climate Change (29)
- Composites (13)
- Computer Science (57)
- Coronavirus (15)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Decarbonization (13)
- Exascale Computing (4)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (4)
- Grid (25)
- High-Performance Computing (23)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (3)
- ITER (4)
- Materials (68)
- Materials Science (54)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (6)
- Nanotechnology (24)
- National Security (10)
- Net Zero (3)
- Neutron Science (41)
- Nuclear Energy (35)
- Partnerships (7)
- Physics (10)
- Polymers (14)
- Quantum Computing (6)
- Quantum Science (14)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (12)
- Software (1)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Sustainable Energy (56)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (1)
- Transportation (47)
Media Contacts

Using additive manufacturing, scientists experimenting with tungsten at Oak Ridge National Laboratory hope to unlock new potential of the high-performance heat-transferring material used to protect components from the plasma inside a fusion reactor. Fusion requires hydrogen isotopes to reach millions of degrees.
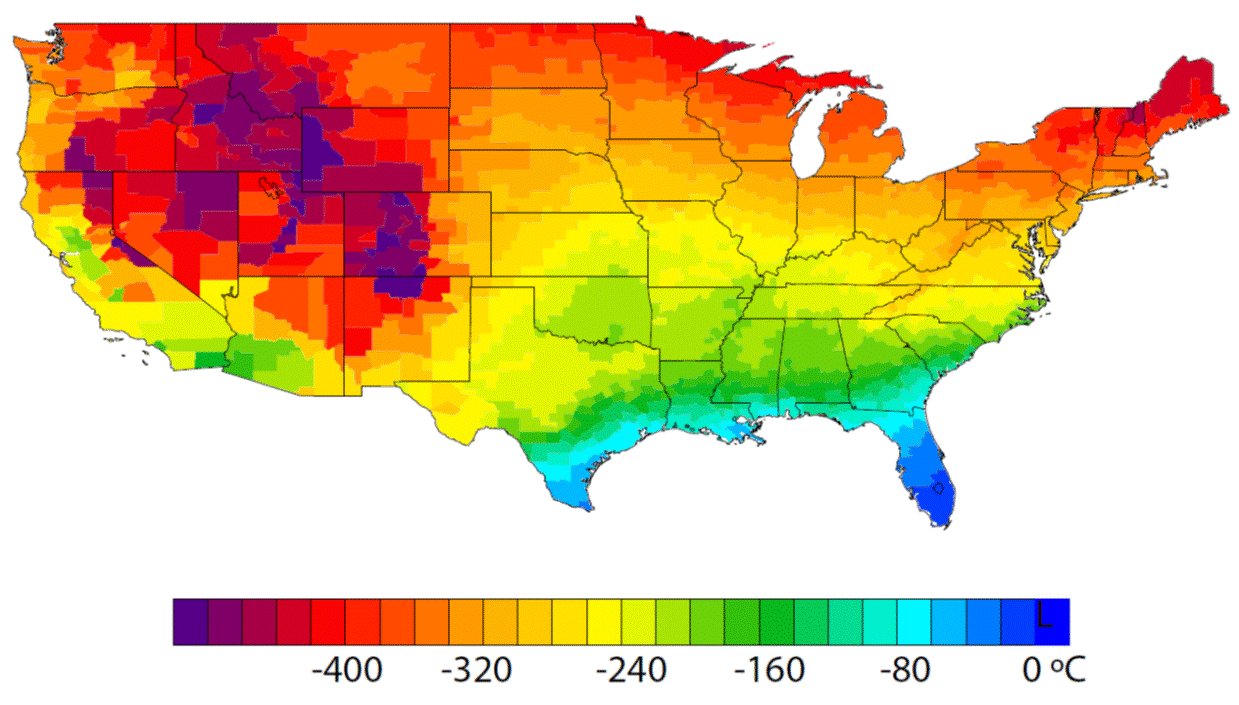
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns

Using the Titan supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, a team of astrophysicists created a set of galactic wind simulations of the highest resolution ever performed. The simulations will allow researchers to gather and interpret more accurate, detailed data that elucidates how galactic winds affect the formation and evolution of galaxies.

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are taking inspiration from neural networks to create computers that mimic the human brain—a quickly growing field known as neuromorphic computing.
A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that designed synthetic polymers can serve as a high-performance binding material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.

For the first time, Oak Ridge National Laboratory has completed testing of nuclear fuels using MiniFuel, an irradiation vehicle that allows for rapid experimentation.

A study led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory explored the interface between the Department of Veterans Affairs’ healthcare data system and the data itself to detect the likelihood of errors and designed an auto-surveillance tool
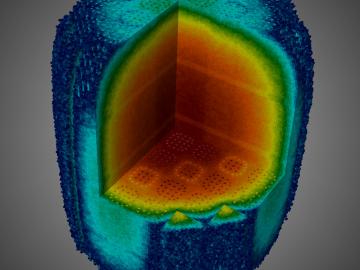
In a step toward advancing small modular nuclear reactor designs, scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have run reactor simulations on ORNL supercomputer Summit with greater-than-expected computational efficiency.
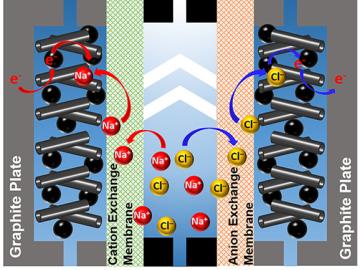
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory used carbon nanotubes to improve a desalination process that attracts and removes ionic compounds such as salt from water using charged electrodes.
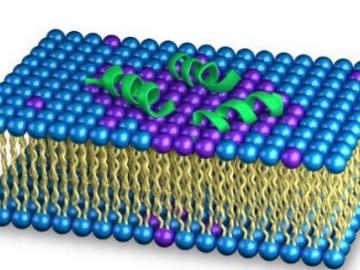
As the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria known as superbugs threatens public health, Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Shuo Qian and Veerendra Sharma from the Bhaba Atomic Research Centre in India are using neutron scattering to study how an antibacterial peptide interacts with and fights harmful bacteria.