
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Biology and Environment (21)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (2)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Energy Science (37)
- Fusion and Fission (7)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (10)
- Materials (94)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (14)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (17)
- Neutron Science (25)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Supercomputing (29)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (28)
- (-) Chemical Sciences (48)
- (-) Clean Water (16)
- (-) Cybersecurity (20)
- (-) Isotopes (25)
- (-) Materials Science (90)
- (-) Nanotechnology (41)
- (-) National Security (21)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (82)
- Advanced Reactors (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (51)
- Big Data (25)
- Bioenergy (42)
- Biology (47)
- Biotechnology (14)
- Buildings (36)
- Composites (23)
- Computer Science (105)
- Coronavirus (28)
- Critical Materials (23)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (75)
- Environment (86)
- Exascale Computing (14)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (17)
- Fusion (26)
- Grid (38)
- High-Performance Computing (44)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (5)
- Machine Learning (27)
- Materials (96)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (5)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (28)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Neutron Science (81)
- Nuclear Energy (47)
- Partnerships (33)
- Physics (30)
- Polymers (23)
- Quantum Computing (18)
- Quantum Science (42)
- Security (13)
- Simulation (19)
- Space Exploration (13)
- Statistics (2)
- Summit (30)
- Transportation (62)
Media Contacts
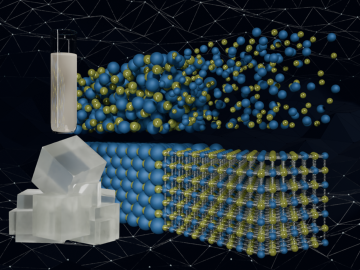
Scientists have developed a new machine learning approach that accurately predicted critical and difficult-to-compute properties of molten salts, materials with diverse nuclear energy applications.

Researchers at ORNL have developed an innovative new technique using carbon nanofibers to enhance binding in carbon fiber and other fiber-reinforced polymer composites – an advance likely to improve structural materials for automobiles, airplanes and other applications that require lightweight and strong materials.

As demand for energy-intensive computing grows, researchers at ORNL have developed a new technique that lets scientists see how interfaces move in promising materials for computing and other applications. The method, now available to users at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences at ORNL, could help design dramatically more energy-efficient technologies.
Scientists at ORNL have developed a method that can track chemical changes in molten salt in real time — helping to pave the way for the deployment of molten salt reactors for energy production.

Working at nanoscale dimensions, billionths of a meter in size, a team of scientists led by ORNL revealed a new way to measure high-speed fluctuations in magnetic materials. Knowledge obtained by these new measurements could be used to advance technologies ranging from traditional computing to the emerging field of quantum computing.

By editing the polymers of discarded plastics, ORNL chemists have found a way to generate new macromolecules with more valuable properties than those of the starting material.

P&G is using simulations on the ORNL Summit supercomputer to study how surfactants in cleaners cause eye irritation. By modeling the corneal epithelium, P&G aims to develop safer, concentrated cleaning products that meet performance and safety standards while supporting sustainability goals.

A chemical reaction can convert two polluting greenhouse gases into valuable building blocks for cleaner fuels and feedstocks, but the high temperature required for the reaction also deactivates the catalyst. A team led by ORNL has found a way to thwart deactivation. The strategy may apply broadly to other catalysts.

Researchers have identified a molecule essential for the microbial conversion of inorganic mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury, moving closer to blocking the dangerous pollutant before it forms.

The Department of Energy has awarded an $88.8 million contract to Hensel Phelps for the construction of a facility to enrich stable isotopes at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.


