
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Energy Science (45)
- (-) Neutron Science (67)
- (-) Nuclear Science and Technology (6)
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (19)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (13)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (68)
- Materials for Computing (9)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (18)
- Quantum information Science (4)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (63)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (7)
- (-) Biomedical (12)
- (-) Computer Science (23)
- (-) Critical Materials (8)
- (-) Machine Learning (6)
- (-) Microscopy (7)
- (-) Neutron Science (64)
- (-) Physics (9)
- (-) Security (4)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (55)
- Advanced Reactors (8)
- Big Data (3)
- Bioenergy (18)
- Biology (11)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (21)
- Chemical Sciences (12)
- Clean Water (5)
- Composites (15)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Cybersecurity (4)
- Energy Storage (49)
- Environment (30)
- Exascale Computing (2)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (2)
- Fusion (4)
- Grid (24)
- High-Performance Computing (4)
- Hydropower (2)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials (36)
- Materials Science (36)
- Mathematics (1)
- Mercury (2)
- Molten Salt (4)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (5)
- Nuclear Energy (20)
- Partnerships (8)
- Polymers (10)
- Quantum Science (5)
- Simulation (2)
- Space Exploration (7)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (5)
- Transportation (45)
Media Contacts
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory found that while all regions of the country can expect an earlier start to the growing season as temperatures rise, the trend is likely to become more variable year-over-year in hotter regions.

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.

To better determine the potential energy cost savings among connected homes, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a computer simulation to more accurately compare energy use on similar weather days.
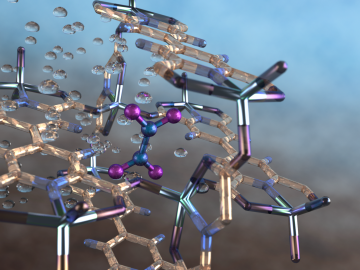
An international team of scientists, led by the University of Manchester, has developed a metal-organic framework, or MOF, material

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have received five 2019 R&D 100 Awards, increasing the lab’s total to 221 since the award’s inception in 1963.
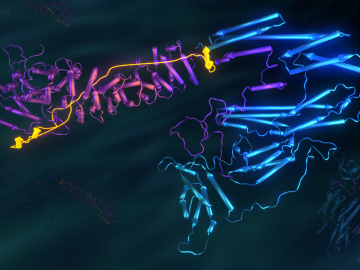
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source and High Flux Isotope Reactor to better understand how certain cells in human tissue bond together.

Using the Titan supercomputer and the Spallation Neutron Source at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, scientists have created the most accurate 3D model yet of an intrinsically disordered protein, revealing the ensemble of its atomic-level structures.

Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to probe the structure of a colorful new material that may pave the way for improved sensors and vivid displays.

IDEMIA Identity & Security USA has licensed an advanced optical array developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The portable technology can be used to help identify individuals in challenging outdoor conditions.
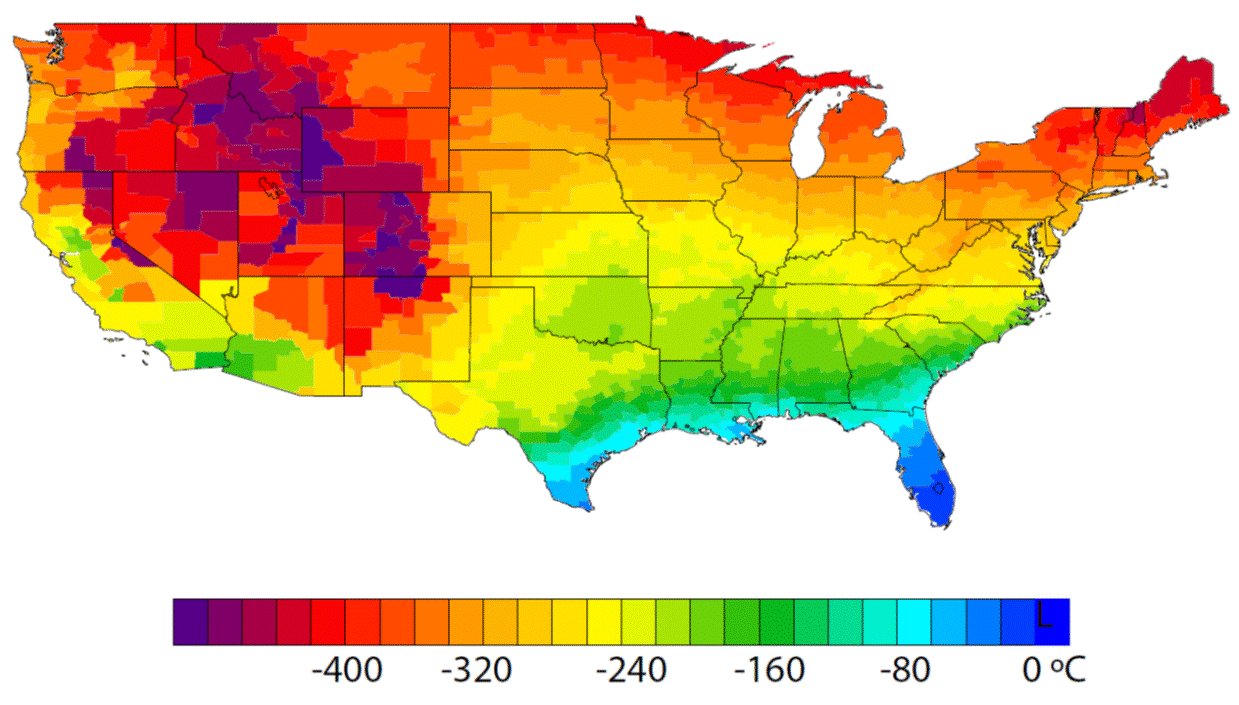
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns


