Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (34)
- Clean Energy (52)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (3)
- Fusion and Fission (1)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (33)
- Materials for Computing (10)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (10)
- Neutron Science (15)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (40)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (39)
- (-) Biomedical (28)
- (-) Clean Water (15)
- (-) Composites (18)
- (-) Coronavirus (28)
- (-) Machine Learning (24)
- (-) Polymers (21)
- (-) Security (12)
- (-) Summit (27)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (74)
- Advanced Reactors (23)
- Artificial Intelligence (43)
- Big Data (24)
- Biology (39)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (31)
- Chemical Sciences (38)
- Climate Change (44)
- Computer Science (97)
- Critical Materials (23)
- Cybersecurity (20)
- Decarbonization (27)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (72)
- Environment (78)
- Exascale Computing (10)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (16)
- Fusion (23)
- Grid (36)
- High-Performance Computing (39)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (23)
- ITER (5)
- Materials (92)
- Materials Science (83)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (5)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (27)
- Molten Salt (7)
- Nanotechnology (38)
- National Security (21)
- Net Zero (5)
- Neutron Science (76)
- Nuclear Energy (45)
- Partnerships (28)
- Physics (28)
- Quantum Computing (13)
- Quantum Science (36)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Simulation (15)
- Space Exploration (13)
- Statistics (2)
- Sustainable Energy (75)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (4)
- Transportation (60)
Media Contacts
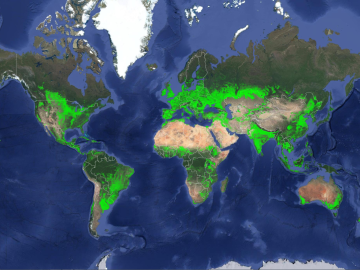
ORNL climate modeling expertise contributed to a project that assessed global emissions of ammonia from croplands now and in a warmer future, while also identifying solutions tuned to local growing conditions.
Corning uses neutron scattering to study the stability of different types of glass. Recently, researchers for the company have found that understanding the stability of the rings of atoms in glass materials can help predict the performance of glass products.

Electric vehicles can drive longer distances if their lithium-ion batteries deliver more energy in a lighter package. A prime weight-loss candidate is the current collector, a component that often adds 10% to the weight of a battery cell without contributing energy.
A team from DOE’s Oak Ridge, Los Alamos and Sandia National Laboratories has developed a new solver algorithm that reduces the total run time of the Model for Prediction Across Scales-Ocean, or MPAS-Ocean, E3SM’s ocean circulation model, by 45%.

Four scientists affiliated with ORNL were named Battelle Distinguished Inventors during the lab’s annual Innovation Awards on Dec. 1 in recognition of being granted 14 or more United States patents.

Scientists at ORNL used their expertise in quantum biology, artificial intelligence and bioengineering to improve how CRISPR Cas9 genome editing tools work on organisms like microbes that can be modified to produce renewable fuels and chemicals.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists identified a gene “hotspot” in the poplar tree that triggers dramatically increased root growth. The discovery supports development of better bioenergy crops and other plants that can thrive in difficult conditions while storing more carbon belowground.

The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory announced the establishment of the Center for AI Security Research, or CAISER, to address threats already present as governments and industries around the world adopt artificial intelligence and take advantage of the benefits it promises in data processing, operational efficiencies and decision-making.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists studied hot springs on different continents and found similarities in how some microbes adapted despite their geographic diversity.

A licensing agreement between the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and research partner ZEISS will enable industrial X-ray computed tomography, or CT, to perform rapid evaluations of 3D-printed components using ORNL’s machine