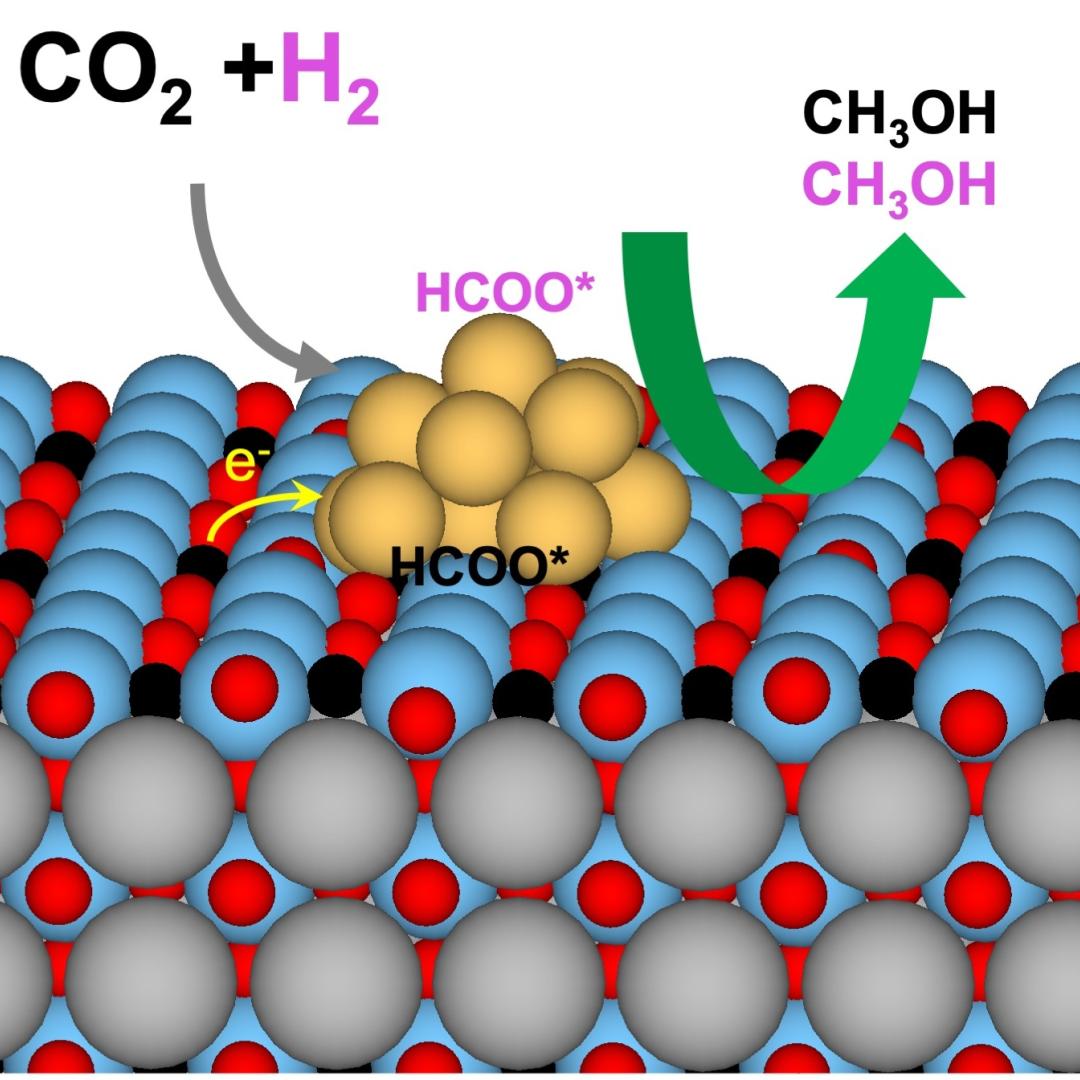
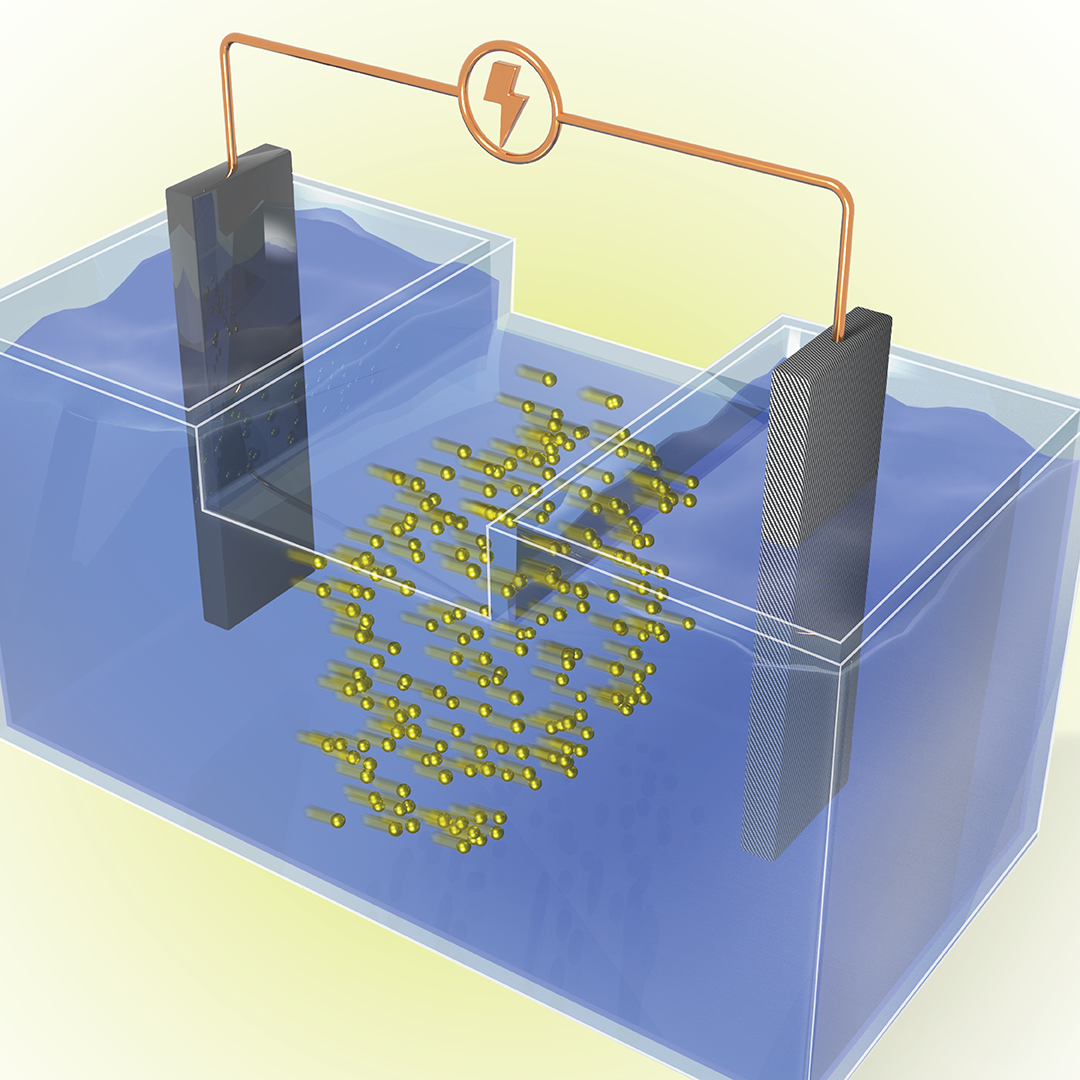
Filter News
Area of Research
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Big Data (20)
- (-) Materials Science (43)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (42)
- Advanced Reactors (15)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Bioenergy (31)
- Biology (37)
- Biomedical (19)
- Biotechnology (6)
- Buildings (26)
- Chemical Sciences (15)
- Clean Water (19)
- Climate Change (34)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (51)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Decarbonization (21)
- Energy Storage (44)
- Environment (79)
- Exascale Computing (3)
- Frontier (3)
- Fusion (16)
- Grid (27)
- High-Performance Computing (19)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (13)
- ITER (4)
- Machine Learning (14)
- Materials (41)
- Mathematics (4)
- Mercury (7)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (18)
- National Security (18)
- Net Zero (3)
- Neutron Science (35)
- Nuclear Energy (32)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (20)
- Polymers (13)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (10)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Sustainable Energy (55)
- Transportation (47)
Media Contacts
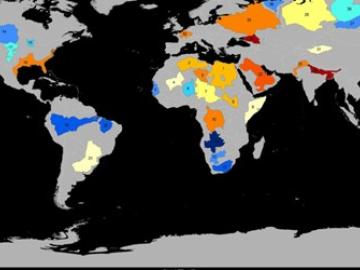
Groundwater withdrawals are expected to peak in about one-third of the world’s basins by 2050, potentially triggering significant trade and agriculture shifts, a new analysis finds.
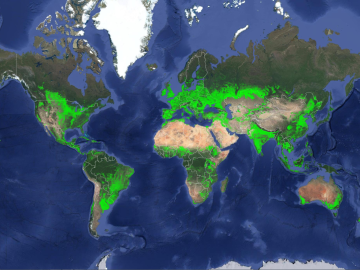
ORNL climate modeling expertise contributed to a project that assessed global emissions of ammonia from croplands now and in a warmer future, while also identifying solutions tuned to local growing conditions.


Madhavi Martin brings a physicist’s tools and perspective to biological and environmental research at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, supporting advances in bioenergy, soil carbon storage and environmental monitoring, and even helping solve a murder mystery.
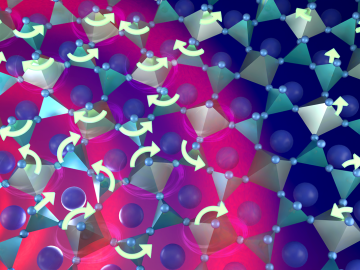
Warming a crystal of the mineral fresnoite, ORNL scientists discovered that excitations called phasons carried heat three times farther and faster than phonons, the excitations that usually carry heat through a material.
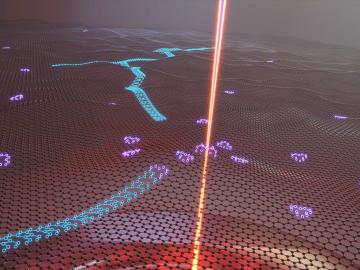
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers serendipitously discovered when they automated the beam of an electron microscope to precisely drill holes in the atomically thin lattice of graphene, the drilled holes closed up.

Chemical and environmental engineer Samarthya Bhagia is focused on achieving carbon neutrality and a circular economy by designing new plant-based materials for a range of applications from energy storage devices and sensors to environmentally friendly bioplastics.
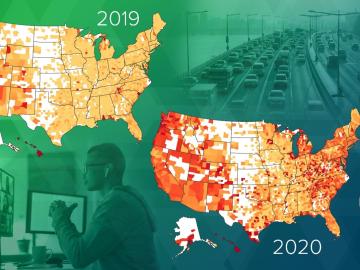
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have empirically quantified the shifts in routine daytime activities, such as getting a morning coffee or takeaway dinner, following safer at home orders during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory is debuting a small satellite ground station that uses high-performance computing to support automated detection of changes to Earth’s landscape.

Several electrolyte and thin-film coating technologies, developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, have been licensed by BTRY, a battery technology company based in Virginia, to make batteries with increased energy density, at lower cost, and with an improved safety profile in crashes.