
Filter News
Area of Research
- Biology and Environment (41)
- Clean Energy (25)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (1)
- Fusion and Fission (2)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotopes (10)
- Materials (23)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (1)
- Neutron Science (3)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (2)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (15)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (19)
- (-) Environment (80)
- (-) Isotopes (15)
- (-) Nanotechnology (18)
- (-) Physics (20)
- (-) Quantum Computing (5)
- (-) Summit (8)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (43)
- Advanced Reactors (15)
- Artificial Intelligence (17)
- Big Data (22)
- Bioenergy (32)
- Biology (38)
- Biomedical (19)
- Biotechnology (7)
- Buildings (28)
- Chemical Sciences (18)
- Climate Change (37)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (52)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Decarbonization (23)
- Energy Storage (45)
- Exascale Computing (4)
- Frontier (4)
- Fusion (16)
- Grid (27)
- High-Performance Computing (20)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (4)
- Machine Learning (15)
- Materials (42)
- Materials Science (45)
- Mathematics (5)
- Mercury (7)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (5)
- National Security (18)
- Net Zero (3)
- Neutron Science (35)
- Nuclear Energy (33)
- Partnerships (1)
- Polymers (14)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (11)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Sustainable Energy (57)
- Transportation (47)
Media Contacts

With the rise of the global pandemic, Omar Demerdash, a Liane B. Russell Distinguished Staff Fellow at ORNL since 2018, has become laser-focused on potential avenues to COVID-19 therapies.
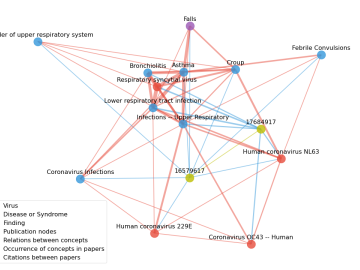
Scientists have tapped the immense power of the Summit supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to comb through millions of medical journal articles to identify potential vaccines, drugs and effective measures that could suppress or stop the
An international team of scientists found that rules governing plant growth hold true even at the edges of the world in the Arctic tundra.

While some of her earth system modeling colleagues at ORNL face challenges such as processor allocation or debugging code, Verity Salmon prepares for mosquito swarms and the possibility of grizzly bears.

In the Physics Division of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, James (“Mitch”) Allmond conducts experiments and uses theoretical models to advance our understanding of the structure of atomic nuclei, which are made of various combinations of protons and neutrons (nucleons).

As a teenager, Kat Royston had a lot of questions. Then an advanced-placement class in physics convinced her all the answers were out there.

A novel approach developed by scientists at ORNL can scan massive datasets of large-scale satellite images to more accurately map infrastructure – such as buildings and roads – in hours versus days.
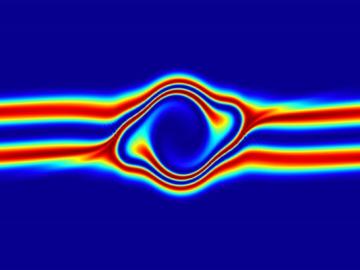
The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.
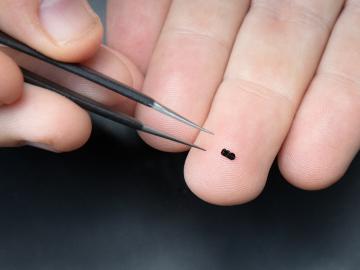
Liam Collins was drawn to study physics to understand “hidden things” and honed his expertise in microscopy so that he could bring them to light.

While Tsouris’ water research is diverse in scope, its fundamentals are based on basic science principles that remain largely unchanged, particularly in a mature field like chemical engineering.


