Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (12)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (51)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Clean Energy (62)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (1)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (24)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (2)
- Neutron Science (4)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (5)
- Supercomputing (10)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (44)
- (-) Bioenergy (33)
- (-) Clean Water (19)
- (-) Composites (12)
- (-) Environment (80)
- (-) Frontier (4)
- (-) Molten Salt (5)
- (-) Nanotechnology (18)
- (-) Space Exploration (10)
- Advanced Reactors (15)
- Artificial Intelligence (17)
- Big Data (23)
- Biology (40)
- Biomedical (20)
- Biotechnology (7)
- Buildings (28)
- Chemical Sciences (19)
- Climate Change (37)
- Computer Science (53)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (14)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Decarbonization (24)
- Energy Storage (45)
- Exascale Computing (4)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion (16)
- Grid (28)
- High-Performance Computing (20)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (15)
- ITER (4)
- Machine Learning (16)
- Materials (42)
- Materials Science (46)
- Mathematics (6)
- Mercury (7)
- Microscopy (20)
- National Security (19)
- Net Zero (4)
- Neutron Science (35)
- Nuclear Energy (34)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (20)
- Polymers (14)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (11)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Sustainable Energy (58)
- Transportation (47)
Media Contacts

Peter Wang is focused on robotics and automation at the Department of Energy’s Manufacturing Demonstration Facility at ORNL, working on high-profile projects such as the MedUSA, a large-scale hybrid additive manufacturing machine.
Liam Collins was drawn to study physics to understand “hidden things” and honed his expertise in microscopy so that he could bring them to light.

While Tsouris’ water research is diverse in scope, its fundamentals are based on basic science principles that remain largely unchanged, particularly in a mature field like chemical engineering.

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory demonstrated that an additively manufactured polymer layer, when applied to carbon fiber reinforced plastic, or CFRP, can serve as an effective protector against aircraft lightning strikes.
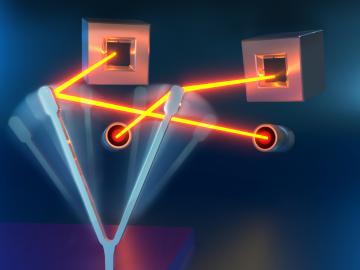
Researchers at ORNL and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory took inspiration from flying insects to demonstrate a miniaturized gyroscope, a special sensor used in navigation technologies.

If humankind reaches Mars this century, an Oak Ridge National Laboratory-developed experiment testing advanced materials for spacecraft may play a key role.
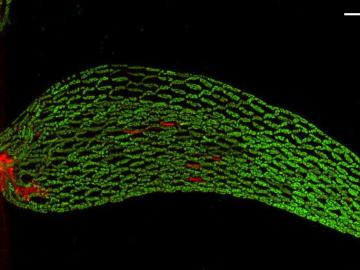
A team of scientists found that critical interactions between microbes and peat moss break down under warming temperatures, impacting moss health and ultimately carbon stored in soil.
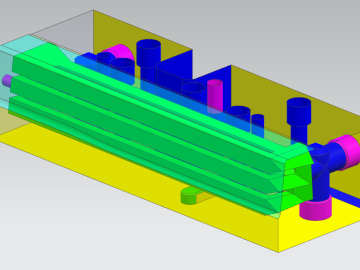
Researchers demonstrated that an additively manufactured hot stamping die can withstand up to 25,000 usage cycles, proving that this technique is a viable solution for production.

Elizabeth Herndon believes in going the distance whether she is preparing to compete in the 2020 Olympic marathon trials or examining how metals move through the environment as a geochemist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

As a computational hydrologist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Ethan Coon combines his talent for math with his love of coding to solve big science questions about water quality, water availability for energy production, climate change, and the