
Filter News
Area of Research
- Biology and Environment (20)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (10)
- Energy Science (22)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (8)
- Materials for Computing (1)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (23)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Supercomputing (19)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (14)
- (-) Computer Science (42)
- (-) Cybersecurity (3)
- (-) Environment (48)
- (-) High-Performance Computing (12)
- (-) Isotopes (5)
- (-) Neutron Science (27)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Big Data (17)
- Bioenergy (17)
- Biology (21)
- Biomedical (11)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (21)
- Chemical Sciences (13)
- Composites (11)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (32)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (9)
- Grid (22)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (3)
- Machine Learning (14)
- Materials (36)
- Materials Science (34)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (11)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (3)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Partnerships (2)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (10)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Quantum Science (11)
- Security (1)
- Simulation (9)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Transportation (36)
Media Contacts

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

To better determine the potential energy cost savings among connected homes, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a computer simulation to more accurately compare energy use on similar weather days.
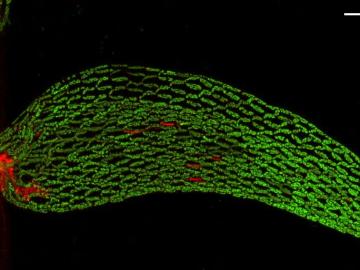
A team of scientists found that critical interactions between microbes and peat moss break down under warming temperatures, impacting moss health and ultimately carbon stored in soil.
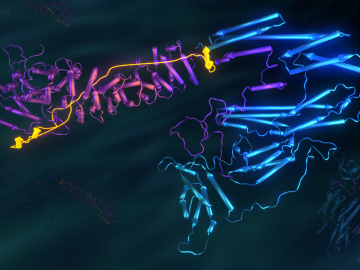
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source and High Flux Isotope Reactor to better understand how certain cells in human tissue bond together.

In collaboration with the Department of Veterans Affairs, a team at Oak Ridge National Laboratory has expanded a VA-developed predictive computing model to identify veterans at risk of suicide and sped it up to run 300 times faster, a gain that could profoundly affect the VA’s ability to reach susceptible veterans quickly.

Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to probe the structure of a colorful new material that may pave the way for improved sensors and vivid displays.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory is training next-generation cameras called dynamic vision sensors, or DVS, to interpret live information—a capability that has applications in robotics and could improve autonomous vehicle sensing.
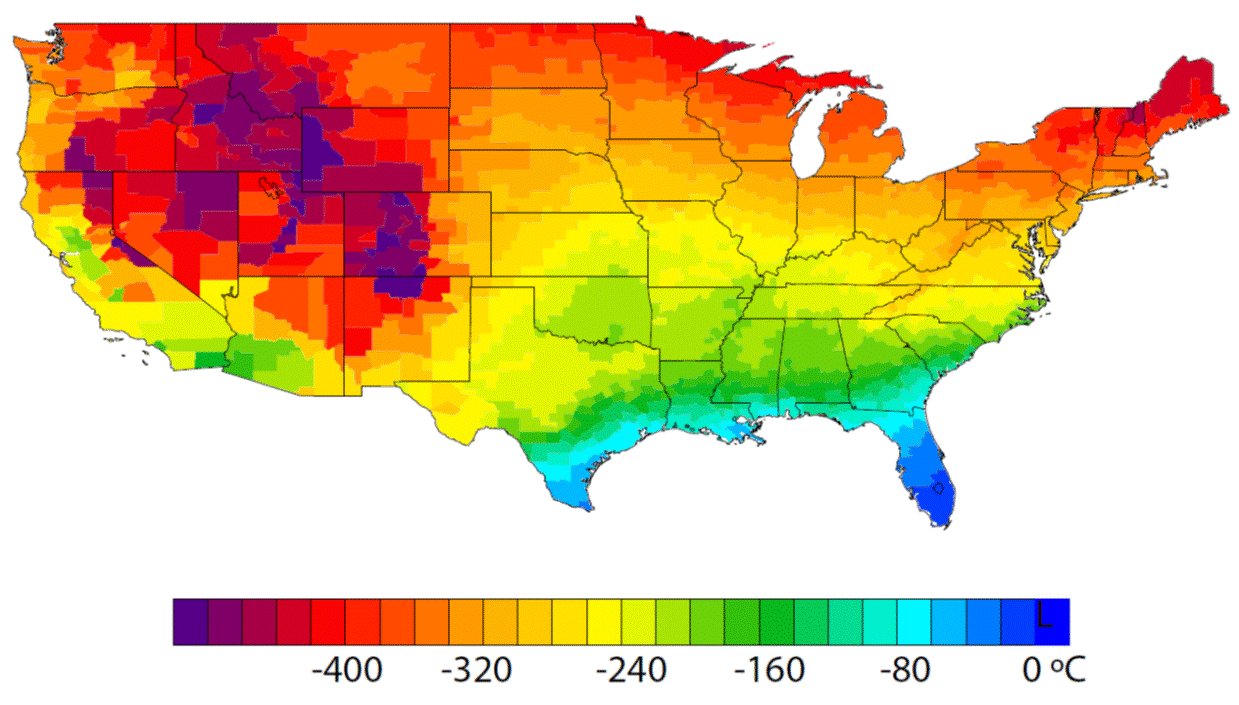
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns

Using the Titan supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, a team of astrophysicists created a set of galactic wind simulations of the highest resolution ever performed. The simulations will allow researchers to gather and interpret more accurate, detailed data that elucidates how galactic winds affect the formation and evolution of galaxies.

A new method developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory improves the energy efficiency of a desalination process known as solar-thermal evaporation.


