Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (25)
- Clean Energy (25)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (1)
- Materials (7)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (2)
- Neutron Science (2)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Supercomputing (8)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (16)
- (-) Composites (9)
- (-) Environment (44)
- (-) Molten Salt (5)
- (-) Quantum Computing (4)
- (-) Security (1)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (31)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (13)
- Big Data (17)
- Biology (18)
- Biomedical (11)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (20)
- Chemical Sciences (11)
- Clean Water (13)
- Climate Change (23)
- Computer Science (40)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Decarbonization (10)
- Energy Storage (31)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (9)
- Grid (21)
- High-Performance Computing (11)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (5)
- ITER (3)
- Machine Learning (12)
- Materials (35)
- Materials Science (34)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (11)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (3)
- Net Zero (2)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (9)
- Quantum Science (10)
- Simulation (7)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (6)
- Sustainable Energy (45)
- Transportation (35)
Media Contacts

A team including Oak Ridge National Laboratory and University of Tennessee researchers demonstrated a novel 3D printing approach called Z-pinning that can increase the material’s strength and toughness by more than three and a half times compared to conventional additive manufacturing processes.
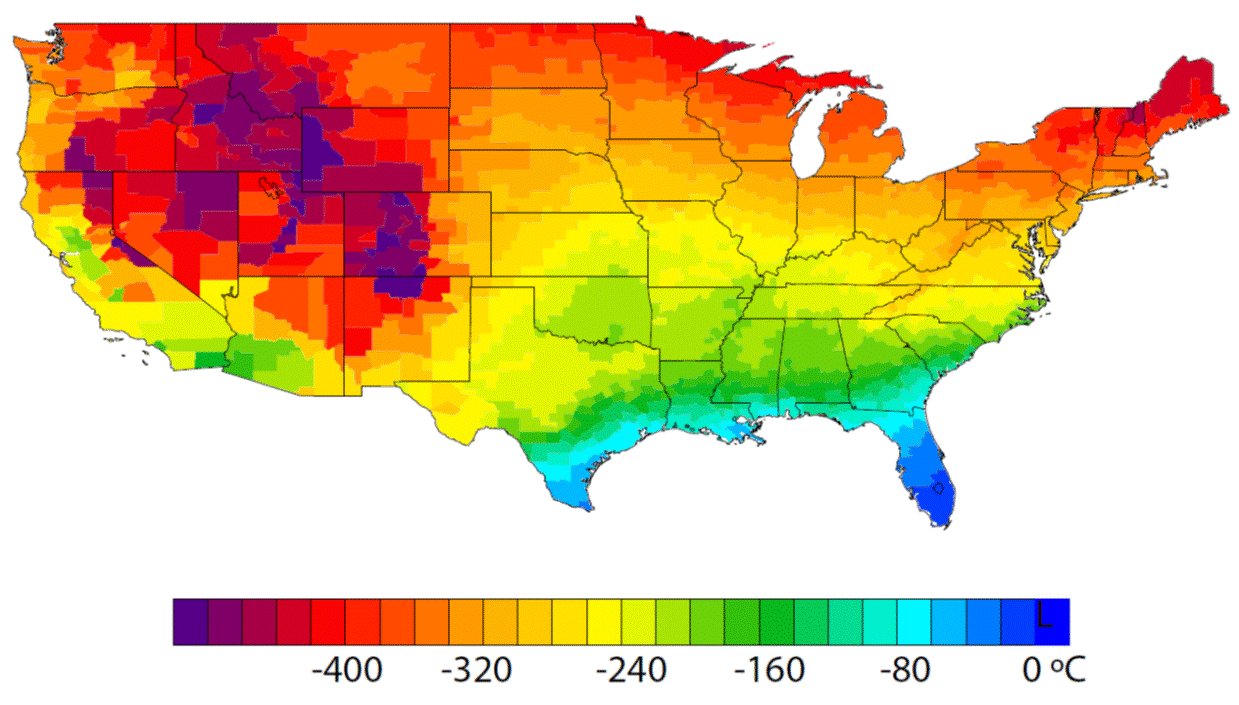
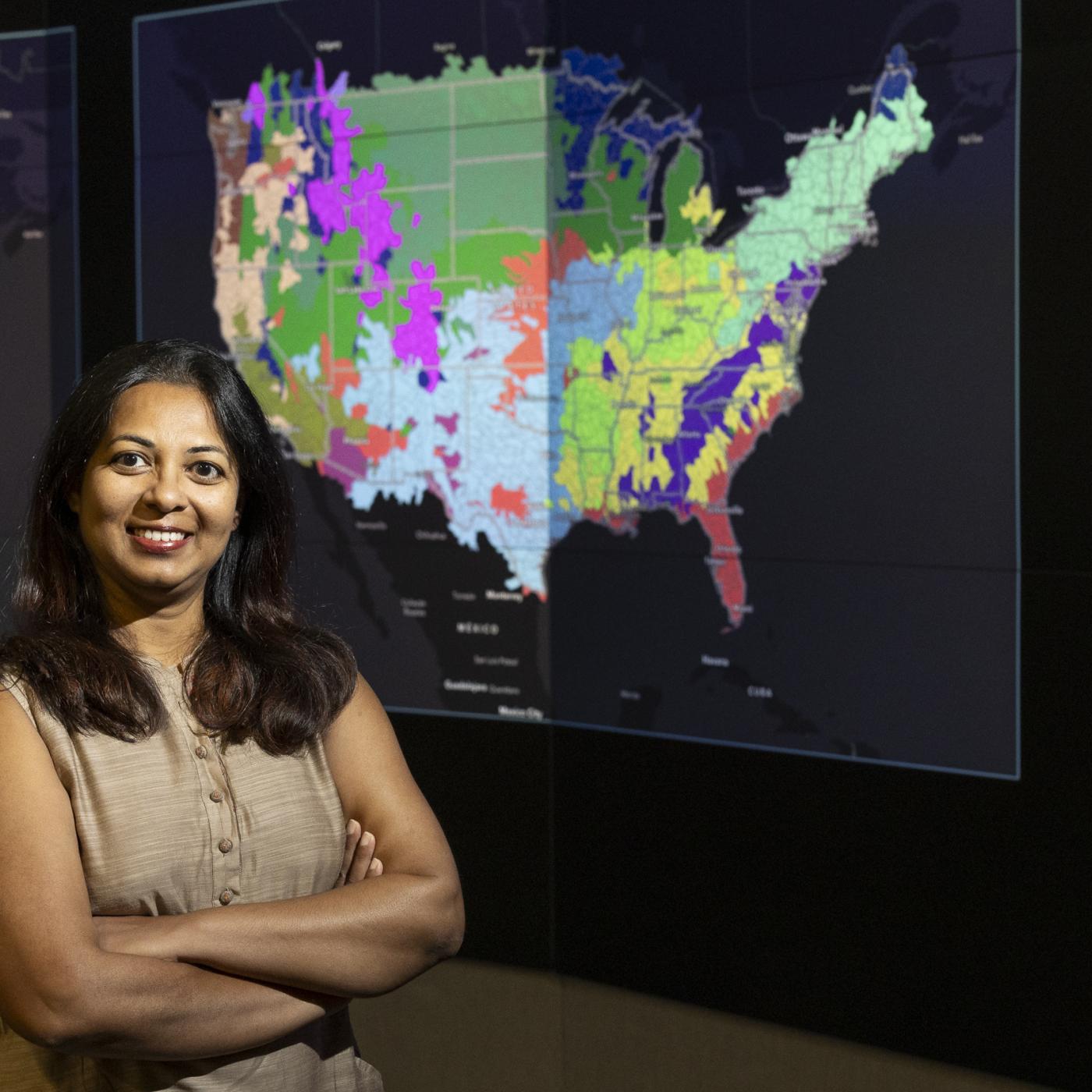
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns
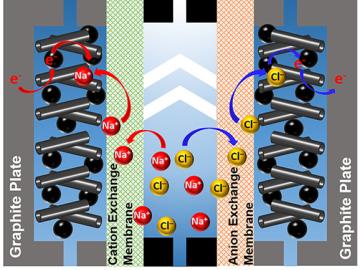
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory used carbon nanotubes to improve a desalination process that attracts and removes ionic compounds such as salt from water using charged electrodes.
Higher carbon dioxide levels caused 30 percent more wood growth in young forest stands across the temperate United States over a decade, according to an analysis led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
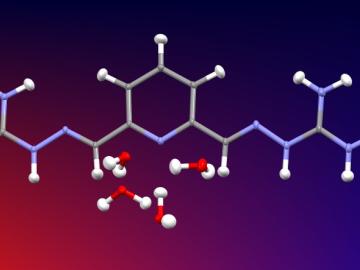
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to investigate the effectiveness of a novel crystallization method to capture carbon dioxide directly from the air.
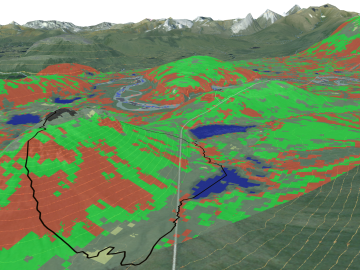
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory used machine learning methods to generate a high-resolution map of vegetation growing in the remote reaches of the Alaskan tundra.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists analyzed more than 50 years of data showing puzzlingly inconsistent trends about corrosion of structural alloys in molten salts and found one factor mattered most—salt purity.

Scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory performed a corrosion test in a neutron radiation field to support the continued development of molten salt reactors.

Thought leaders from across the maritime community came together at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to explore the emerging new energy landscape for the maritime transportation system during the Ninth Annual Maritime Risk Symposium.

Biologists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center have confirmed that microorganisms called methanogens can transform mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury with varying efficiency across species.


