Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Isotopes (5)
- (-) Simulation (6)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (30)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (13)
- Big Data (15)
- Bioenergy (15)
- Biology (17)
- Biomedical (11)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (17)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Clean Water (13)
- Climate Change (20)
- Composites (9)
- Computer Science (39)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Critical Materials (11)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Decarbonization (7)
- Energy Storage (30)
- Environment (43)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (9)
- Grid (20)
- High-Performance Computing (11)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (3)
- Machine Learning (10)
- Materials (34)
- Materials Science (31)
- Mathematics (1)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (11)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (3)
- Net Zero (1)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Energy (18)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (4)
- Quantum Science (10)
- Security (1)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (6)
- Sustainable Energy (42)
- Transportation (35)
Media Contacts
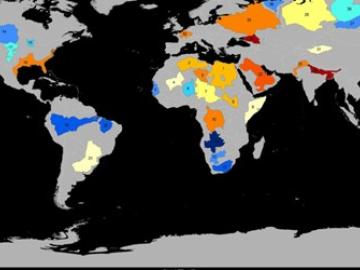
Groundwater withdrawals are expected to peak in about one-third of the world’s basins by 2050, potentially triggering significant trade and agriculture shifts, a new analysis finds.
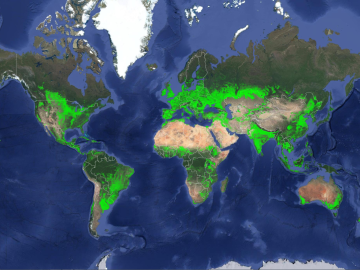
ORNL climate modeling expertise contributed to a project that assessed global emissions of ammonia from croplands now and in a warmer future, while also identifying solutions tuned to local growing conditions.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists led the development of a supply chain model revealing the optimal places to site farms, biorefineries, pipelines and other infrastructure for sustainable aviation fuel production.

When aging vehicle batteries lack the juice to power your car anymore, they may still hold energy. Yet it’s tough to find new uses for lithium-ion batteries with different makers, ages and sizes. A solution is urgently needed because battery recycling options are scarce.
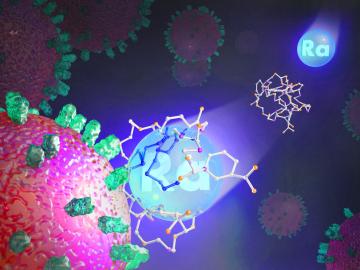
Researchers at ORNL explored radium’s chemistry to advance cancer treatments using ionizing radiation.
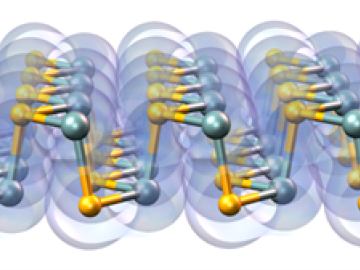
A multi-lab research team led by ORNL's Paul Kent is developing a computer application called QMCPACK to enable precise and reliable predictions of the fundamental properties of materials critical in energy research.

To advance sensor technologies, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers studied piezoelectric materials, which convert mechanical stress into electrical energy, to see how they could handle bombardment with energetic neutrons.

An Oak Ridge National Laboratory researcher has invented a version of an isotope-separating device that can withstand extreme environments, including radiation and chemical solvents.

A better way of welding targets for Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s plutonium-238 production has sped up the process and improved consistency and efficiency. This advancement will ultimately benefit the lab’s goal to make enough Pu-238 – the isotope that powers NASA’s deep space missions – to yield 1.5 kilograms of plutonium oxide annually by 2026.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have discovered a better way to separate actinium-227, a rare isotope essential for an FDA-approved cancer treatment.