
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (102)
- (-) Supercomputing (111)
- Advanced Manufacturing (22)
- Biology and Environment (31)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (5)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (139)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (10)
- Fusion Energy (3)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (17)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- National Security (28)
- Neutron Science (33)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (7)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (26)
- (-) Cybersecurity (8)
- (-) Frontier (32)
- (-) Grid (9)
- (-) Materials Science (83)
- (-) Quantum Computing (21)
- (-) Summit (43)
- Advanced Reactors (5)
- Artificial Intelligence (39)
- Big Data (22)
- Bioenergy (18)
- Biology (14)
- Biomedical (22)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (8)
- Chemical Sciences (32)
- Clean Water (3)
- Composites (9)
- Computer Science (99)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (15)
- Energy Storage (37)
- Environment (35)
- Exascale Computing (26)
- Fusion (8)
- High-Performance Computing (45)
- Irradiation (1)
- Isotopes (14)
- ITER (1)
- Machine Learning (15)
- Materials (79)
- Mathematics (2)
- Microscopy (29)
- Molten Salt (3)
- Nanotechnology (42)
- National Security (8)
- Neutron Science (42)
- Nuclear Energy (20)
- Partnerships (11)
- Physics (34)
- Polymers (18)
- Quantum Science (33)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (16)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (5)
- Transportation (19)
Media Contacts
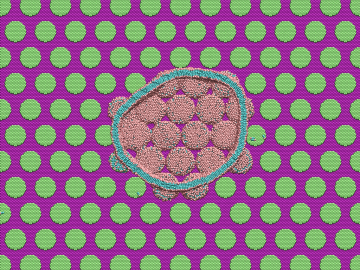
Over the past decade, teams of engineers, chemists and biologists have analyzed the physical and chemical properties of cicada wings, hoping to unlock the secret of their ability to kill microbes on contact. If this function of nature can be replicated by science, it may lead to products with inherently antibacterial surfaces that are more effective than current chemical treatments.

With the world’s first exascale supercomputer now fully open for scientific business, researchers can thank the early users who helped get the machine up to speed.
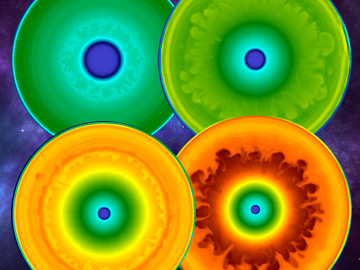
As a result of largescale 3D supernova simulations conducted on the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility’s Summit supercomputer by researchers from the University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, astrophysicists now have the most complete picture yet of what gravitational waves from exploding stars look like.

Scientist-inventors from ORNL will present seven new technologies during the Technology Innovation Showcase on Friday, July 14, from 8 a.m.–4 p.m. at the Joint Institute for Computational Sciences on ORNL’s campus.

An advance in a topological insulator material — whose interior behaves like an electrical insulator but whose surface behaves like a conductor — could revolutionize the fields of next-generation electronics and quantum computing, according to scientists at ORNL.

To support the development of a revolutionary new open fan engine architecture for the future of flight, GE Aerospace has run simulations using the world’s fastest supercomputer capable of crunching data in excess of exascale speed, or more than a quintillion calculations per second.

In late May, the Quantum Science Center convened its first in-person all-hands meeting since the center was established in 2020. More than 120 QSC members gathered in Nashville, Tennessee to discuss the center’s operations, research and overarching scientific aims.
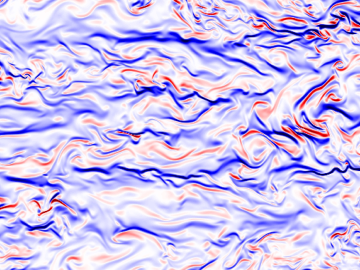
Simulations performed on the Summit supercomputer at ORNL revealed new insights into the role of turbulence in mixing fluids and could open new possibilities for projecting climate change and studying fluid dynamics.

Innovations in artificial intelligence are rapidly shaping our world, from virtual assistants and chatbots to self-driving cars and automated manufacturing.

Rigoberto Advincula, a renowned scientist at ORNL and professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Tennessee, has won the Netzsch North American Thermal Analysis Society Fellows Award for 2023.


