
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) National Security (30)
- (-) Supercomputing (59)
- Advanced Manufacturing (8)
- Biology and Environment (68)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Clean Energy (139)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (9)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (44)
- Fusion Energy (16)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (72)
- Materials for Computing (8)
- Neutron Science (28)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (41)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (2)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (2)
- (-) Big Data (22)
- (-) Coronavirus (16)
- (-) Decarbonization (6)
- (-) Fusion (2)
- (-) Grid (11)
- (-) Machine Learning (23)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (8)
- (-) Physics (8)
- (-) Sustainable Energy (12)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (7)
- Artificial Intelligence (45)
- Bioenergy (11)
- Biology (14)
- Biomedical (17)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (4)
- Chemical Sciences (5)
- Climate Change (20)
- Computer Science (104)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Cybersecurity (23)
- Energy Storage (9)
- Environment (25)
- Exascale Computing (22)
- Frontier (28)
- High-Performance Computing (40)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (16)
- Materials Science (17)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (11)
- National Security (35)
- Net Zero (1)
- Neutron Science (15)
- Partnerships (4)
- Polymers (2)
- Quantum Computing (19)
- Quantum Science (25)
- Security (14)
- Simulation (14)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (3)
- Summit (42)
- Transportation (8)
Media Contacts
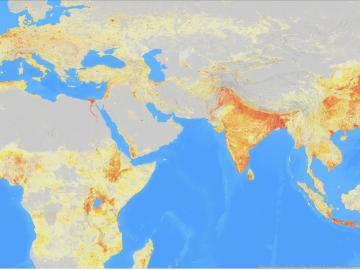
It’s a simple premise: To truly improve the health, safety, and security of human beings, you must first understand where those individuals are.
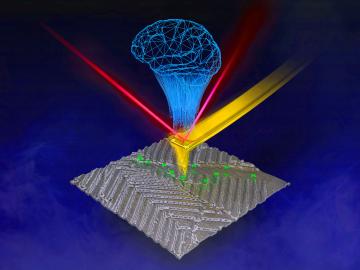
Researchers at ORNL are teaching microscopes to drive discoveries with an intuitive algorithm, developed at the lab’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, that could guide breakthroughs in new materials for energy technologies, sensing and computing.
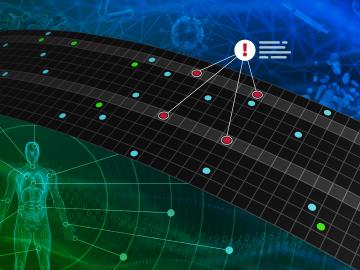
A team of researchers has developed a novel, machine learning–based technique to explore and identify relationships among medical concepts using electronic health record data across multiple healthcare providers.

Tackling the climate crisis and achieving an equitable clean energy future are among the biggest challenges of our time.

Unequal access to modern infrastructure is a feature of growing cities, according to a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
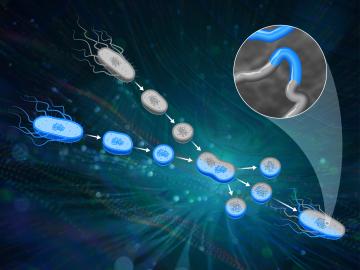
ORNL scientists had a problem mapping the genomes of bacteria to better understand the origins of their physical traits and improve their function for bioenergy production.

A force within the supercomputing community, Jack Dongarra developed software packages that became standard in the industry, allowing high-performance computers to become increasingly more powerful in recent decades.

A study led by researchers at ORNL used the nation’s fastest supercomputer to close in on the answer to a central question of modern physics that could help conduct development of the next generation of energy technologies.
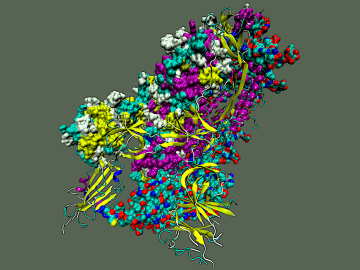
To explore the inner workings of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, or SARS-CoV-2, researchers from ORNL developed a novel technique.
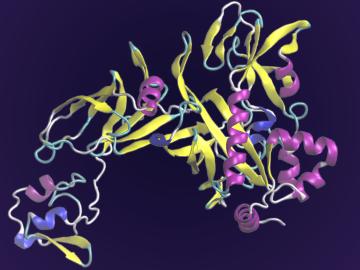
A team of scientists led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Georgia Institute of Technology is using supercomputing and revolutionary deep learning tools to predict the structures and roles of thousands of proteins with unknown functions.


