Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Fusion Energy (2)
- (-) Materials for Computing (5)
- Advanced Manufacturing (22)
- Biology and Environment (25)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Clean Energy (87)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Materials (31)
- National Security (16)
- Neutron Science (16)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Supercomputing (74)
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- (-) Summit (2)
- Advanced Reactors (7)
- Bioenergy (1)
- Biology (1)
- Biomedical (2)
- Chemical Sciences (4)
- Climate Change (1)
- Composites (1)
- Computer Science (9)
- Coronavirus (3)
- Decarbonization (1)
- Energy Storage (4)
- Environment (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (13)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (11)
- Materials Science (17)
- Microscopy (4)
- Nanotechnology (7)
- National Security (1)
- Neutron Science (5)
- Nuclear Energy (10)
- Polymers (6)
- Quantum Computing (1)
- Quantum Science (3)
- Security (1)
- Simulation (1)
- Space Exploration (1)
- Sustainable Energy (7)
- Transportation (5)
Media Contacts

Researchers at ORNL designed a novel polymer to bind and strengthen silica sand for binder jet additive manufacturing, a 3D-printing method used by industries for prototyping and part production.
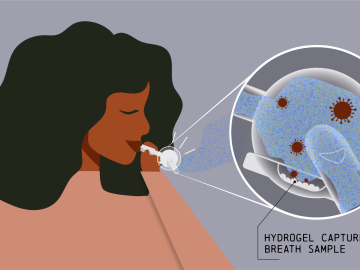
Collaborators at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee Health Science Center are developing a breath-sampling whistle that could make COVID-19 screening easy to do at home.
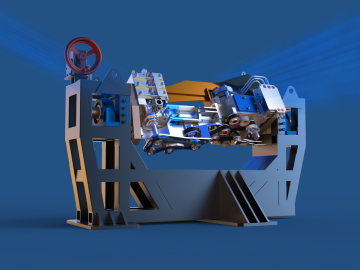
In the quest for advanced vehicles with higher energy efficiency and ultra-low emissions, ORNL researchers are accelerating a research engine that gives scientists and engineers an unprecedented view inside the atomic-level workings of combustion engines in real time.
Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee designed and demonstrated a method to make carbon-based materials that can be used as electrodes compatible with a specific semiconductor circuitry.

Four research teams from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and their technologies have received 2020 R&D 100 Awards.
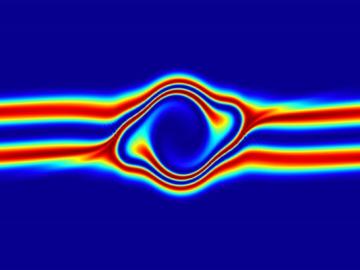
The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

Using additive manufacturing, scientists experimenting with tungsten at Oak Ridge National Laboratory hope to unlock new potential of the high-performance heat-transferring material used to protect components from the plasma inside a fusion reactor. Fusion requires hydrogen isotopes to reach millions of degrees.