
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) National Security (38)
- (-) Neutron Science (112)
- (-) Nuclear Science and Technology (41)
- Advanced Manufacturing (13)
- Biological Systems (2)
- Biology and Environment (106)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Clean Energy (158)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (16)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (2)
- Fusion and Fission (34)
- Fusion Energy (14)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (8)
- Materials (194)
- Materials Characterization (2)
- Materials for Computing (24)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- Mathematics (1)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (2)
- Quantum information Science (8)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (137)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (12)
- (-) Big Data (8)
- (-) Bioenergy (10)
- (-) Climate Change (5)
- (-) Computer Science (33)
- (-) Grid (6)
- (-) Materials (16)
- (-) Materials Science (27)
- (-) Nanotechnology (11)
- (-) Neutron Science (101)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (41)
- (-) Physics (11)
- (-) Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (12)
- Artificial Intelligence (18)
- Biology (9)
- Biomedical (15)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (1)
- Chemical Sciences (4)
- Clean Water (2)
- Composites (1)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Cybersecurity (19)
- Decarbonization (5)
- Energy Storage (8)
- Environment (13)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (2)
- Fusion (10)
- High-Performance Computing (6)
- Isotopes (5)
- Machine Learning (15)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (3)
- Molten Salt (4)
- National Security (34)
- Partnerships (4)
- Polymers (1)
- Quantum Computing (1)
- Quantum Science (8)
- Security (12)
- Simulation (1)
- Space Exploration (8)
- Summit (7)
- Sustainable Energy (5)
- Transportation (7)
Media Contacts

Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have new experimental evidence and a predictive theory that solves a long-standing materials science mystery: why certain crystalline materials shrink when heated.

If humankind reaches Mars this century, an Oak Ridge National Laboratory-developed experiment testing advanced materials for spacecraft may play a key role.

Jason Nattress, an Alvin M. Weinberg Fellow at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, found his calling on a nuclear submarine.

Two of the researchers who share the Nobel Prize in Chemistry announced Wednesday—John B. Goodenough of the University of Texas at Austin and M. Stanley Whittingham of Binghamton University in New York—have research ties to ORNL.
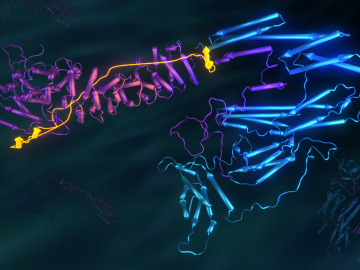
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source and High Flux Isotope Reactor to better understand how certain cells in human tissue bond together.
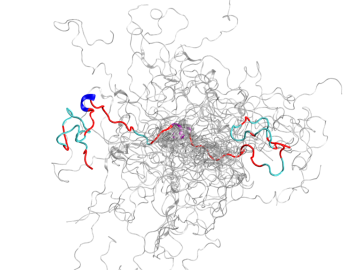
Using the Titan supercomputer and the Spallation Neutron Source at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, scientists have created the most accurate 3D model yet of an intrinsically disordered protein, revealing the ensemble of its atomic-level structures.

Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to probe the structure of a colorful new material that may pave the way for improved sensors and vivid displays.

Ask Tyler Gerczak to find a negative in working at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and his only complaint is the summer weather. It is not as forgiving as the summers in Pulaski, Wisconsin, his hometown.
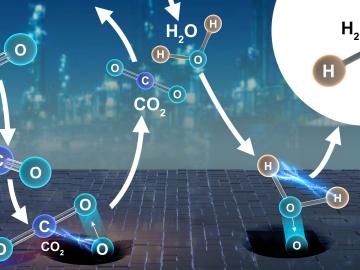
Collaborators at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and U.S. universities used neutron scattering and other advanced characterization techniques to study how a prominent catalyst enables the “water-gas shift” reaction to purify and generate hydrogen at industrial scale.
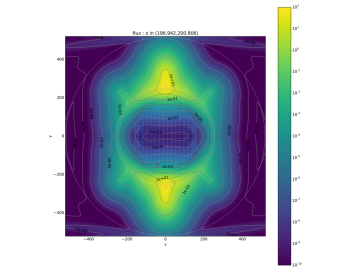
Researchers have developed high-fidelity modeling capabilities for predicting radiation interactions outside of the reactor core—a tool that could help keep nuclear reactors running longer.


