Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Fusion (7)
- (-) Mercury (3)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (89)
- Advanced Reactors (9)
- Artificial Intelligence (13)
- Big Data (7)
- Bioenergy (30)
- Biology (12)
- Biomedical (10)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (36)
- Chemical Sciences (33)
- Clean Water (10)
- Climate Change (23)
- Composites (19)
- Computer Science (36)
- Coronavirus (14)
- Critical Materials (19)
- Cybersecurity (10)
- Decarbonization (34)
- Energy Storage (86)
- Environment (64)
- Exascale Computing (3)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (3)
- Grid (41)
- High-Performance Computing (9)
- Hydropower (2)
- Irradiation (1)
- Isotopes (13)
- ITER (1)
- Machine Learning (10)
- Materials (94)
- Materials Science (90)
- Mathematics (3)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (29)
- Molten Salt (3)
- Nanotechnology (41)
- National Security (6)
- Net Zero (3)
- Neutron Science (42)
- Nuclear Energy (22)
- Partnerships (16)
- Physics (29)
- Polymers (21)
- Quantum Computing (3)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (4)
- Space Exploration (5)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (6)
- Sustainable Energy (71)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (5)
- Transportation (69)
Media Contacts

Creating energy the way the sun and stars do — through nuclear fusion — is one of the grand challenges facing science and technology. What’s easy for the sun and its billions of relatives turns out to be particularly difficult on Earth.

ORNL will team up with six of eight companies that are advancing designs and research and development for fusion power plants with the mission to achieve a pilot-scale demonstration of fusion within a decade.

Three researchers at ORNL have been named ORNL Corporate Fellows in recognition of significant career accomplishments and continued leadership in their scientific fields.

ORNL's Larry Baylor and Andrew Lupini have been elected fellows of the American Physical Society.

Using additive manufacturing, scientists experimenting with tungsten at Oak Ridge National Laboratory hope to unlock new potential of the high-performance heat-transferring material used to protect components from the plasma inside a fusion reactor. Fusion requires hydrogen isotopes to reach millions of degrees.
Sometimes solutions to the biggest problems can be found in the smallest details. The work of biochemist Alex Johs at Oak Ridge National Laboratory bears this out, as he focuses on understanding protein structures and molecular interactions to resolve complex global problems like the spread of mercury pollution in waterways and the food supply.

Scientists have tested a novel heat-shielding graphite foam, originally created at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, at Germany’s Wendelstein 7-X stellarator with promising results for use in plasma-facing components of fusion reactors.

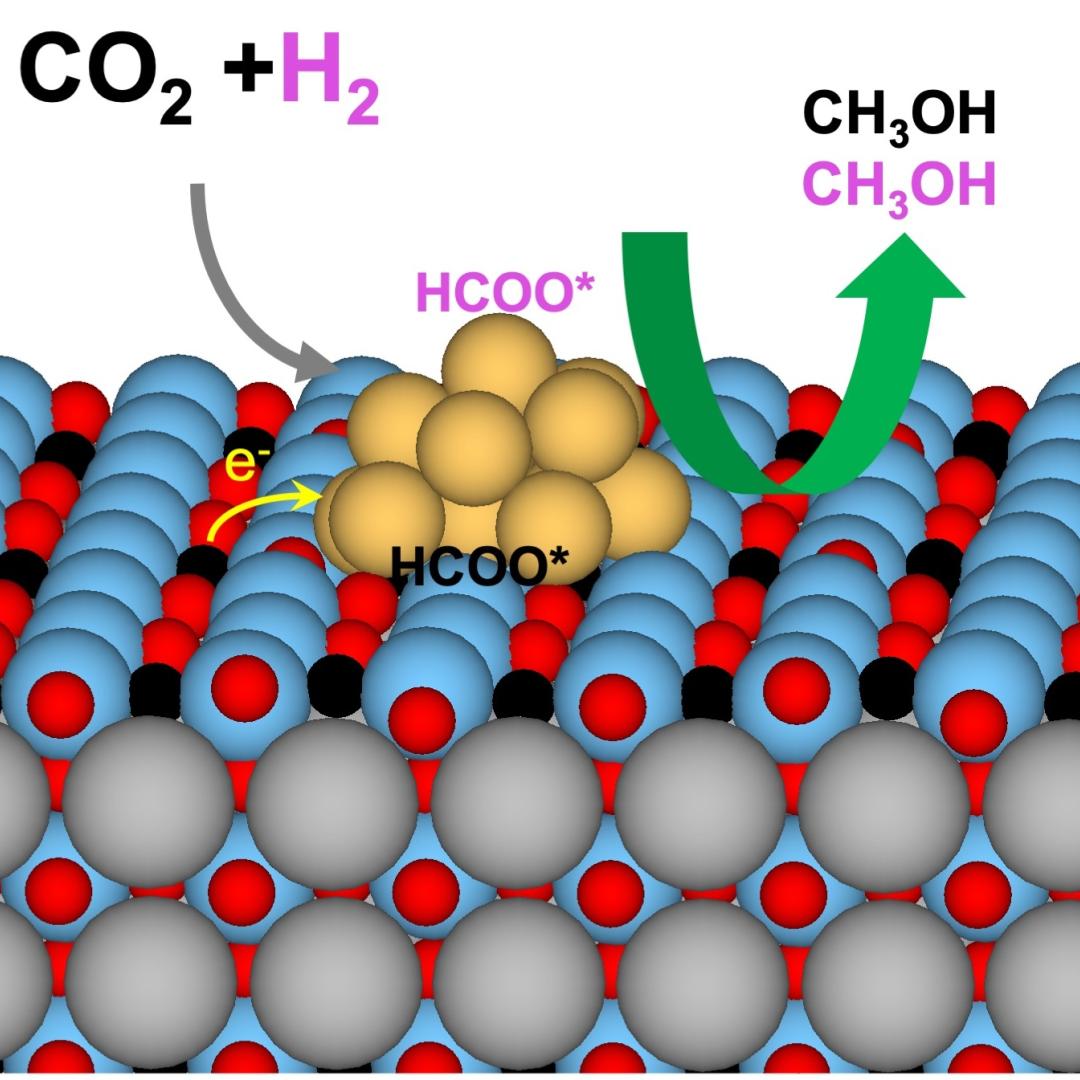
Biologists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center have confirmed that microorganisms called methanogens can transform mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury with varying efficiency across species.

The materials inside a fusion reactor must withstand one of the most extreme environments in science, with temperatures in the thousands of degrees Celsius and a constant bombardment of neutron radiation and deuterium and tritium, isotopes of hydrogen, from the volatile plasma at th...
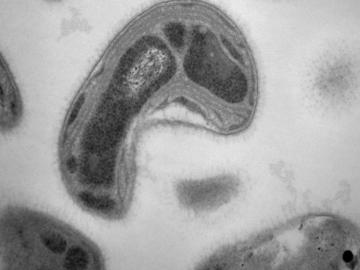
A team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has identified a novel microbial process that can break down toxic methylmercury in the environment, a fundamental scientific discovery that could potentially reduce mercury toxicity levels and sup...