Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (48)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Clean Energy (32)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (2)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (4)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (14)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (43)
- Neutron Science (5)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Supercomputing (35)
News Topics
- (-) Climate Change (100)
- (-) Machine Learning (48)
- (-) Molten Salt (8)
- (-) National Security (62)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (122)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (91)
- Big Data (55)
- Bioenergy (92)
- Biology (99)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (22)
- Buildings (57)
- Chemical Sciences (65)
- Clean Water (29)
- Composites (26)
- Computer Science (189)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (26)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (80)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (109)
- Environment (195)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (6)
- Frontier (42)
- Fusion (55)
- Grid (63)
- High-Performance Computing (85)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (53)
- ITER (7)
- Materials (144)
- Materials Science (141)
- Mathematics (8)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (51)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- Net Zero (14)
- Neutron Science (131)
- Nuclear Energy (109)
- Partnerships (44)
- Physics (61)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (34)
- Quantum Science (69)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (48)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (126)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (97)
Media Contacts
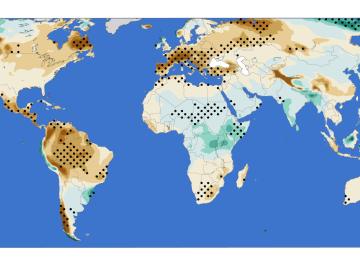
A new analysis from Oak Ridge National Laboratory shows that intensified aridity, or drier atmospheric conditions, is caused by human-driven increases in greenhouse gas emissions. The findings point to an opportunity to address and potentially reverse the trend by reducing emissions.
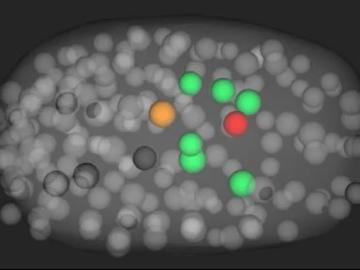
Scientists have developed a novel approach to computationally infer previously undetected behaviors within complex biological environments by analyzing live, time-lapsed images that show the positioning of embryonic cells in C. elegans, or roundworms. Their published methods could be used to reveal hidden biological activity.

A new version of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model, or E3SM, is two times faster than an earlier version released in 2018.

ORNL’s Budhendra “Budhu” Bhaduri has been elected a fellow of the American Association of Geographers. The honor recognizes Bhaduri as “a world leader in innovation, development and application of research in human dynamics, geographic data science, remote sensing and scalable geocomputation.”
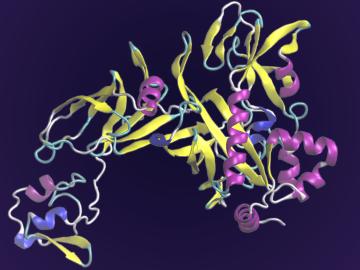
A team of scientists led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Georgia Institute of Technology is using supercomputing and revolutionary deep learning tools to predict the structures and roles of thousands of proteins with unknown functions.

The world is full of “huge, gnarly problems,” as ORNL research scientist and musician Melissa Allen-Dumas puts it — no matter what line of work you’re in. That was certainly the case when she would wrestle with a tough piece of music.
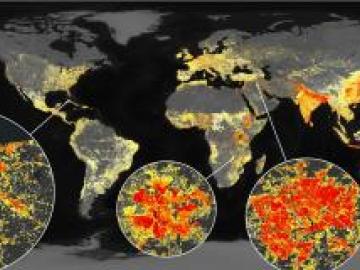
Using novel data sets and computing systems, researchers at ORNL are simulating how climate change affects the safety and security of the country.

Ten scientists from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are among the world’s most highly cited researchers, according to a bibliometric analysis conducted by the scientific publication analytics firm Clarivate.

A team of collaborators from ORNL, Google Inc., Snowflake Inc. and Ververica GmbH has tested a computing concept that could help speed up real-time processing of data that stream on mobile and other electronic devices.

A new modeling capability developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory incorporates important biogeochemical processes happening in river corridors for a clearer understanding of how water quality will be impacted by climate change, land use and


