Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Biotechnology (22)
- (-) Critical Materials (26)
- (-) Statistics (3)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (122)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (91)
- Big Data (55)
- Bioenergy (92)
- Biology (99)
- Biomedical (58)
- Buildings (57)
- Chemical Sciences (65)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (100)
- Composites (26)
- Computer Science (189)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (80)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (109)
- Environment (195)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (6)
- Frontier (42)
- Fusion (55)
- Grid (63)
- High-Performance Computing (85)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (53)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (48)
- Materials (144)
- Materials Science (141)
- Mathematics (8)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (62)
- Net Zero (14)
- Neutron Science (131)
- Nuclear Energy (109)
- Partnerships (44)
- Physics (61)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (34)
- Quantum Science (69)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (48)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (126)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (97)
Media Contacts

From soda bottles to car bumpers to piping, electronics, and packaging, plastics have become a ubiquitous part of our lives.

Momentum Technologies Inc., a Dallas, Texas-based materials science company that is focused on extracting critical metals from electronic waste, has licensed an Oak Ridge National Laboratory process for recovering cobalt and other metals from spent
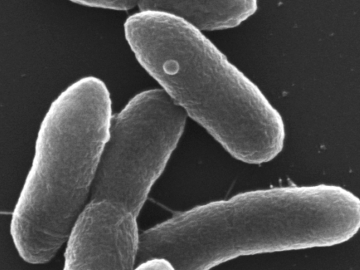
ORNL scientists have modified a single microbe to simultaneously digest five of the most abundant components of lignocellulosic biomass, a big step forward in the development of a cost-effective biochemical conversion process to turn plants into
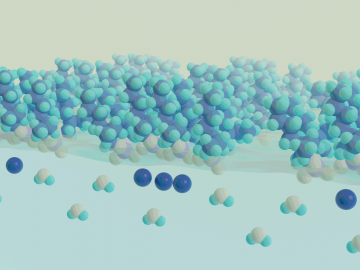
Real-time measurements captured by researchers at ORNL provide missing insight into chemical separations to recover cobalt, a critical raw material used to make batteries and magnets for modern technologies.
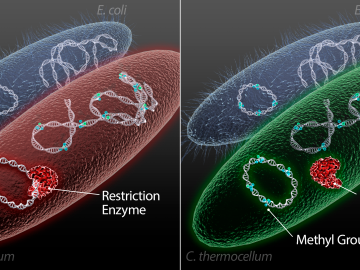
Scientists at the US Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated a method to insert genes into a variety of microorganisms that previously would not accept foreign DNA, with the goal of creating custom microbes to break down plants for bioenergy.
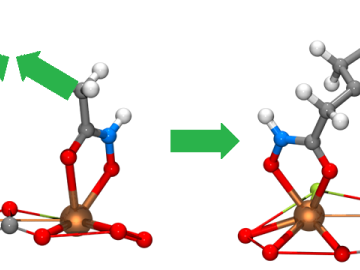
Scientists from the Critical Materials Institute used the Titan supercomputer and Eos computing cluster at ORNL to analyze designer molecules that could increase the yield of rare earth elements found in bastnaesite, an important mineral
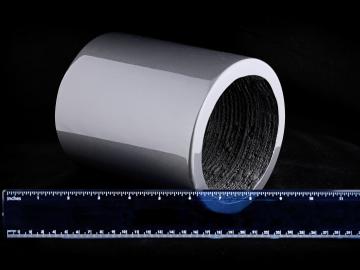
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that permanent magnets produced by additive manufacturing can outperform bonded magnets made using traditional techniques while conserving critical materials. Scientists fabric...

A process developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for large-scale recovery of rare earth magnets from used computer hard drives will undergo industrial testing under a new agreement between Oddello Industries LLC and ORNL, as part of the Department of Energy’s Crit...
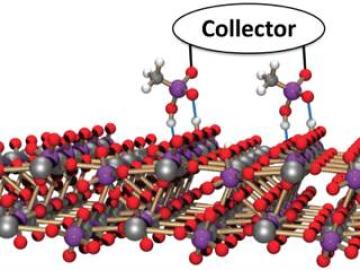
Ensuring a reliable supply of rare earth elements, including four key lanthanides and yttrium, is a major goal of the Critical Materials Institute (https://cmi.ameslab.gov) as these elements are essential to many clean-energy technologies. These include energy-efficient lighting, ...

A new technology developed by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Critical Materials Institute that aids in the recycling, recovery and extraction of rare earth minerals has been licensed to U.S. Rare Earths, Inc.


