Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (22)
- Biology and Environment (84)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Clean Energy (87)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (5)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Materials (28)
- Materials for Computing (5)
- National Security (8)
- Neutron Science (11)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Supercomputing (44)
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (121)
- (-) Biology (98)
- (-) Frontier (42)
- (-) Software (1)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (91)
- Big Data (53)
- Bioenergy (91)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (22)
- Buildings (57)
- Chemical Sciences (63)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (99)
- Composites (26)
- Computer Science (187)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (26)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (79)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (108)
- Environment (194)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Fusion (54)
- Grid (62)
- High-Performance Computing (84)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (53)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (47)
- Materials (144)
- Materials Science (140)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (61)
- Net Zero (13)
- Neutron Science (131)
- Nuclear Energy (108)
- Partnerships (44)
- Physics (61)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (34)
- Quantum Science (69)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (47)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (125)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (97)
Media Contacts
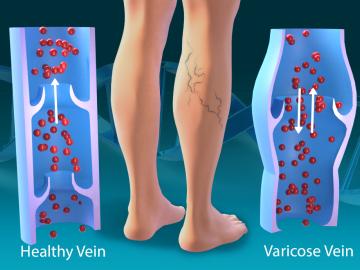
As part of a multi-institutional research project, scientists at ORNL leveraged their computational systems biology expertise and the largest, most diverse set of health data to date to explore the genetic basis of varicose veins.

The Department of Energy’s Center for Bioenergy Innovation, led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory, recently added three new members to its board of directors: Deborah Crawford of the University of Tennessee, Knoxville; Susan Hubbard of ORNL; and Maureen McCann of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.

Merlin Theodore is one of eight new board members announced by President Biden; she will join the 25-member board for a six-year term.
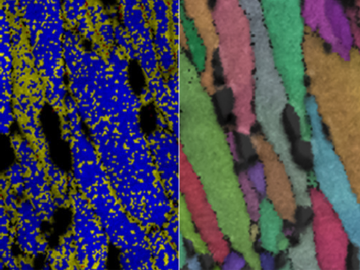
ORNL researchers have identified a mechanism in a 3D-printed alloy – termed “load shuffling” — that could enable the design of better-performing lightweight materials for vehicles.

A team of scientists led by ORNL discovered the gene in agave that governs when the plant goes dormant and used it to create poplar trees that nearly doubled in size, increasing biomass yield for biofuels production

Erica Prates has found a way to help speed the pursuit of healthier ecosystems by linking the function of the smallest molecules to their effects on large-scale processes, leveraging a combination of science, math and computing.

Paul Langan will join ORNL in the spring as associate laboratory director for the Biological and Environmental Systems Science Directorate.

ORNL’s next major computing achievement could open a new universe of scientific possibilities accelerated by the primal forces at the heart of matter and energy.

The interaction of elemental iron with the vast stores of carbon locked away in Arctic soils is key to how greenhouse gases are emitted during thawing and should be included in models used to predict Earth’s climate.
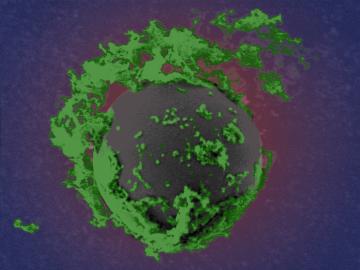
The presence of minerals called ash in plants makes little difference to the fitness of new naturally derived compound materials designed for additive manufacturing, an Oak Ridge National Laboratory-led team found.


