Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (16)
- Clean Energy (17)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (2)
- Fusion and Fission (1)
- Materials (8)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (19)
- Neutron Science (3)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (1)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Supercomputing (30)
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (31)
- (-) Cybersecurity (35)
- (-) Emergency (2)
- (-) Exascale Computing (41)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (126)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (99)
- Big Data (60)
- Bioenergy (92)
- Biology (100)
- Biomedical (60)
- Biotechnology (23)
- Buildings (63)
- Chemical Sciences (71)
- Climate Change (104)
- Composites (29)
- Computer Science (195)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Decarbonization (83)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (112)
- Environment (198)
- Fossil Energy (6)
- Frontier (45)
- Fusion (58)
- Grid (66)
- High-Performance Computing (91)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (56)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (50)
- Materials (146)
- Materials Science (145)
- Mathematics (9)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (9)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (71)
- Net Zero (14)
- Neutron Science (134)
- Nuclear Energy (111)
- Partnerships (50)
- Physics (64)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (37)
- Quantum Science (71)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (25)
- Simulation (50)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (59)
- Sustainable Energy (130)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (97)
Media Contacts

Nuclear physicists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently used Frontier, the world’s most powerful supercomputer, to calculate the magnetic properties of calcium-48’s atomic nucleus.

A study by more than a dozen scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory examines potential strategies to integrate quantum computing with the world’s most powerful supercomputing systems in the pursuit of science.
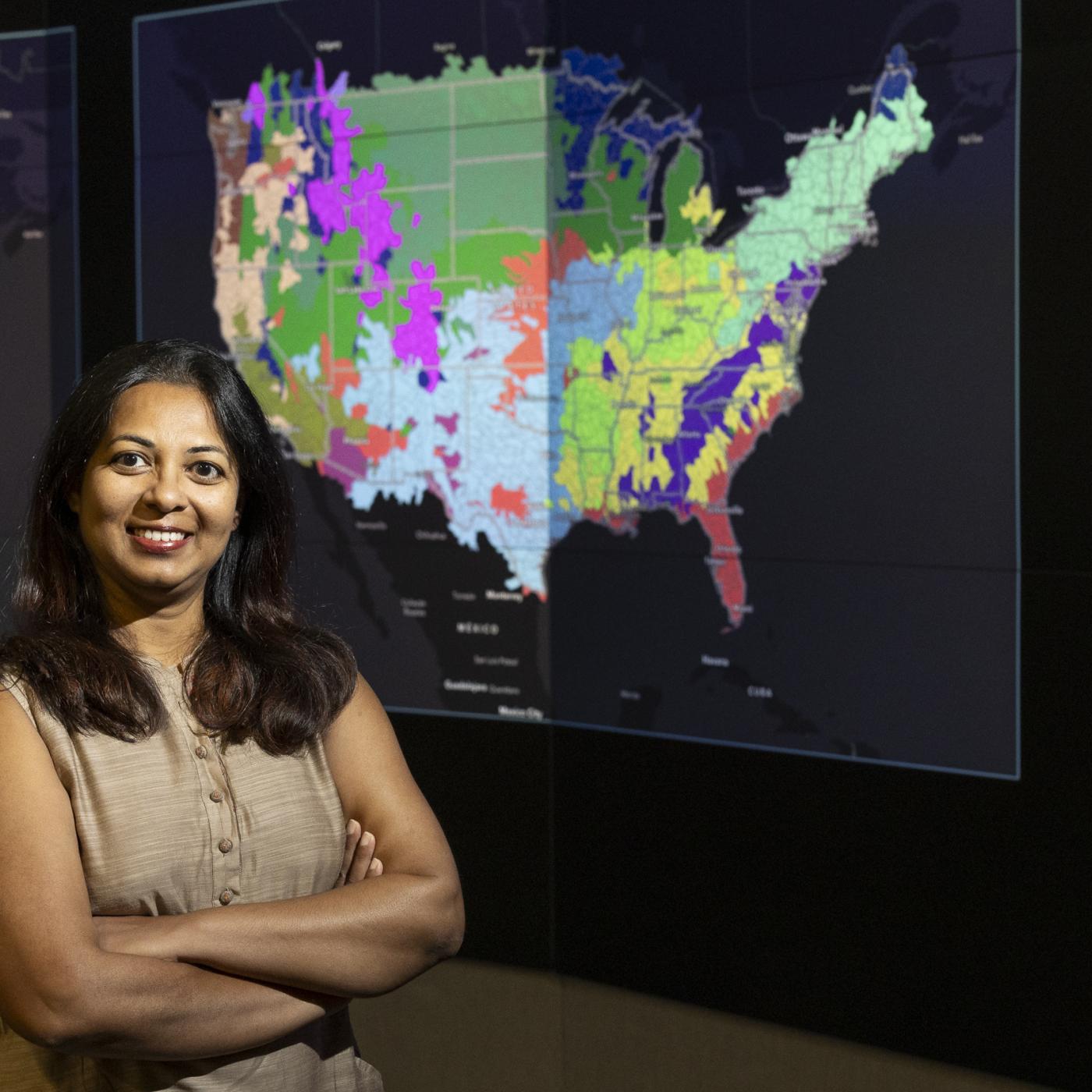
Debjani Singh, a senior scientist at ORNL, leads the HydroSource project, which enhances hydropower research by making water data more accessible and useful. With a background in water resources, data science, and earth science, Singh applies innovative tools like AI to advance research. Her career, shaped by her early exposure to science in India, focuses on bridging research with practical applications.
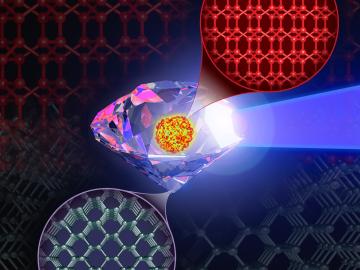
The world’s fastest supercomputer helped researchers simulate synthesizing a material harder and tougher than a diamond — or any other substance on Earth. The study used Frontier to predict the likeliest strategy to synthesize such a material, thought to exist so far only within the interiors of giant exoplanets, or planets beyond our solar system.

To better predict long-term flooding risk, scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a 3D modeling framework that captures the complex dynamics of water as it flows across the landscape. The framework seeks to provide valuable insights into which communities are most vulnerable as the climate changes, and was developed for a project that’s assessing climate risk and mitigation pathways for an urban area along the Southeast Texas coast.

Researchers conduct largest, most accurate molecular dynamics simulations to date of two million correlated electrons using Frontier, the world’s fastest supercomputer. The simulation, which exceed an exaflop using full double precision, is 1,000 times greater in size and speed than any quantum chemistry simulation of it's kind.

John Lagergren, a staff scientist in Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Plant Systems Biology group, is using his expertise in applied math and machine learning to develop neural networks to quickly analyze the vast amounts of data on plant traits amassed at ORNL’s Advanced Plant Phenotyping Laboratory.

A team led by researchers at ORNL explored training strategies for one of the largest artificial intelligence models to date with help from the world’s fastest supercomputer. The findings could help guide training for a new generation of AI models for scientific research.

When scientists pushed the world’s fastest supercomputer to its limits, they found those limits stretched beyond even their biggest expectations. In the latest milestone, a team of engineers and scientists used Frontier to simulate a system of nearly half a trillion atoms — the largest system ever modeled and more than 400 times the size of the closest competition.
Integral to the functionality of ORNL's Frontier supercomputer is its ability to store the vast amounts of data it produces onto its file system, Orion. But even more important to the computational scientists running simulations on Frontier is their capability to quickly write and read to Orion along with effectively analyzing all that data. And that’s where ADIOS comes in.


