Filter News
Area of Research
- Biology and Environment (19)
- Clean Energy (15)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Fusion and Fission (2)
- Isotopes (24)
- Materials (52)
- Materials for Computing (8)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (1)
- Neutron Science (12)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (5)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (11)
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (29)
- (-) Education (4)
- (-) Emergency (2)
- (-) Isotopes (51)
- (-) Nanotechnology (60)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (119)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (91)
- Big Data (51)
- Bioenergy (91)
- Biology (98)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (22)
- Buildings (56)
- Chemical Sciences (62)
- Climate Change (98)
- Composites (26)
- Computer Science (185)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (25)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (78)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (108)
- Environment (194)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Frontier (42)
- Fusion (53)
- Grid (61)
- High-Performance Computing (84)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (47)
- Materials (143)
- Materials Science (138)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- National Security (60)
- Net Zero (13)
- Neutron Science (130)
- Nuclear Energy (105)
- Partnerships (41)
- Physics (59)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (32)
- Quantum Science (67)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (45)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (124)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (95)
Media Contacts

Early career scientist Frankie White's was part of two major isotope projects at the same time he was preparing to be a father. As co-lead on a team that achieved the first synthesis and characterization of a radium compound using single crystal X-ray diffraction and part of a team that characterized the properties of promethium, White reflects on the life-changing timeline at work, and at home.

Lætitia H. Delmau, a distinguished researcher and radiochemist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has received the 2024 Glenn T. Seaborg Actinide Separations Award.

A group of high school graduates and community college students visited ORNL to meet staff and find out just what goes on at a DOE national laboratory. The Job Shadow Day was arranged by tnAchieves, a student support organization that works to increase higher educational opportunities for students across Tennessee through scholarships and mentorship.

Scientists have uncovered the properties of a rare earth element that was first discovered 80 years ago at the very same laboratory, opening a new pathway for the exploration of elements critical in modern technology, from medicine to space travel.

Students from the first class of ORNL and Pellissippi State Community College's joint Chemical Radiation Technology Pathway toured isotope facilities at ORNL.

ORNL scientists are working on a project to engineer and develop a cryogenic ion trap apparatus to simulate quantum spin liquids, a key research area in materials science and neutron scattering studies.
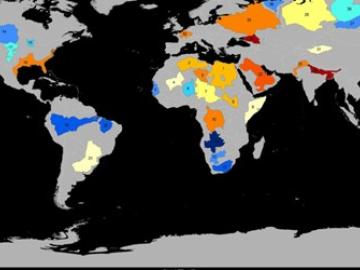
Groundwater withdrawals are expected to peak in about one-third of the world’s basins by 2050, potentially triggering significant trade and agriculture shifts, a new analysis finds.

ORNL researchers modeled how hurricane cloud cover would affect solar energy generation as a storm followed 10 possible trajectories over the Caribbean and Southern U.S.

Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula, a scientist with joint appointments at ORNL and the University of Tennessee, has been named a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering.

SkyNano, an Innovation Crossroads alumnus, held a ribbon-cutting for their new facility. SkyNano exemplifies using DOE resources to build a successful clean energy company, making valuable carbon nanotubes from waste CO2.




