
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Biology and Environment (20)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computer Science (2)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (97)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (2)
- Fusion and Fission (33)
- Fusion Energy (10)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials (103)
- Materials for Computing (13)
- National Security (12)
- Neutron Science (126)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (39)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Supercomputing (28)
News Topics
- (-) Chemical Sciences (86)
- (-) Energy Storage (114)
- (-) Neutron Science (171)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (122)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (146)
- Advanced Reactors (40)
- Artificial Intelligence (131)
- Big Data (79)
- Bioenergy (112)
- Biology (128)
- Biomedical (73)
- Biotechnology (39)
- Buildings (74)
- Clean Water (33)
- Composites (35)
- Computer Science (226)
- Coronavirus (48)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Education (5)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Environment (218)
- Exascale Computing (67)
- Fossil Energy (8)
- Frontier (64)
- Fusion (66)
- Grid (74)
- High-Performance Computing (130)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (62)
- ITER (9)
- Machine Learning (68)
- Materials (157)
- Materials Science (158)
- Mathematics (12)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Microscopy (56)
- Molten Salt (10)
- Nanotechnology (64)
- National Security (86)
- Partnerships (68)
- Physics (69)
- Polymers (35)
- Quantum Computing (53)
- Quantum Science (92)
- Security (31)
- Simulation (65)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (26)
- Statistics (4)
- Summit (71)
- Transportation (103)
Media Contacts

Using LEGO® bricks, Robert Saethre has worked to create a model of the ring injection region of the SNS pulsed accelerator that features the new Proton Power Upgrade magnets and vacuum chambers.
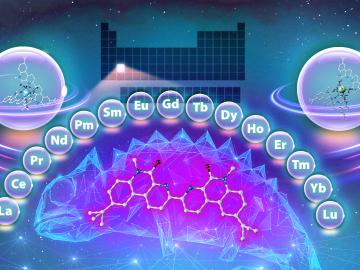
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have found a chemical “chameleon” that could improve the process used to purify rare-earth metals used in clean energy, medical and national security applications.

A team led by scientists at ORNL identified and demonstrated a method to process a plant-based material called nanocellulose that reduced energy needs by a whopping 21%, using simulations on the lab’s supercomputers and follow-on analysis.
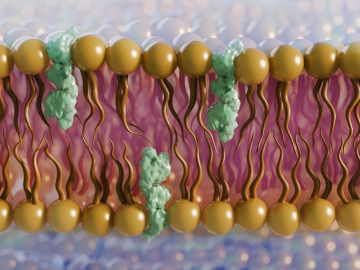
A group of scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have conducted neutron scattering research to reveal key information about fungus cell membranes that could aid in developing new antifungal treatments.

Researchers for the first time documented the specific chemistry dynamics and structure of high-temperature liquid uranium trichloride salt, a potential nuclear fuel source for next-generation reactors.

DOE commissioned a neutron imaging instrument, VENUS, at the Spallation Neutron Source in July. VENUS instrument scientists will use AI to deliver 3D models to researchers in half the time it typically takes.

To speed the arrival of the next-generation solid-state batteries that will power electric vehicles and other technologies, scientists led by ORNL advanced the development of flexible, durable sheets of electrolytes. They used a polymer to create a strong yet springy thin film that binds electrolytic particles and at least doubles energy storage.
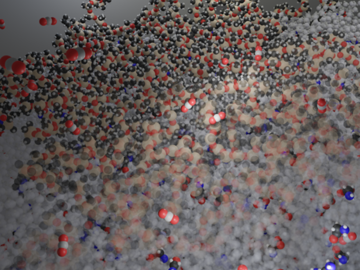
Researchers at ORNL have demonstrated that small molecular tweaks to surfaces can improve absorption technology for direct air capture of carbon dioxide. The team added a charged polymer layer to an amino acid solution, and then, through spectroscopy and simulation, found that the charged layer can hold amino acids at its surface.

At ORNL, a group of scientists used neutron scattering techniques to investigate a relatively new functional material called a Weyl semimetal. These Weyl fermions move very quickly in a material and can carry electrical charge at room temperature. Scientists think that Weyl semimetals, if used in future electronics, could allow electricity to flow more efficiently and enable more energy-efficient computers and other electronic devices.

Benjamin Manard, an analytical chemist in the Chemical Sciences Division of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, will receive the 2024 Lester W. Strock Award from the Society of Applied Spectroscopy.


