Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (14)
- Clean Energy (56)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials (22)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- National Security (8)
- Neutron Science (9)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (5)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (52)
News Topics
- (-) Critical Materials (25)
- (-) Grid (61)
- (-) Space Exploration (25)
- (-) Summit (57)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (117)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (89)
- Big Data (51)
- Bioenergy (89)
- Biology (97)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (22)
- Buildings (55)
- Chemical Sciences (61)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (96)
- Composites (25)
- Computer Science (185)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (76)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (108)
- Environment (193)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Frontier (42)
- Fusion (53)
- High-Performance Computing (84)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (50)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (47)
- Materials (141)
- Materials Science (137)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (60)
- Net Zero (12)
- Neutron Science (130)
- Nuclear Energy (105)
- Partnerships (41)
- Physics (59)
- Polymers (31)
- Quantum Computing (31)
- Quantum Science (66)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (45)
- Software (1)
- Statistics (3)
- Sustainable Energy (122)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (94)
Media Contacts

ORNL researchers used electron-beam additive manufacturing to 3D-print the first complex, defect-free tungsten parts with complex geometries.

Researchers set a new benchmark for future experiments making materials in space rather than for space. They discovered that many kinds of glass have similar atomic structure and arrangements and can successfully be made in space. Scientists from nine institutions in government, academia and industry participated in this 5-year study.
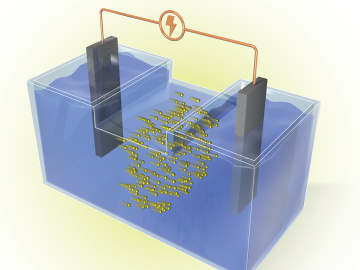
Researchers at ORNL are developing battery technologies to fight climate change in two ways, by expanding the use of renewable energy and capturing airborne carbon dioxide.

ORNL researchers have teamed up with other national labs to develop a free platform called Open Energy Data Initiative Solar Systems Integration Data and Modeling to better analyze the behavior of electric grids incorporating many solar projects.

A collection of seven technologies for lithium recovery developed by scientists from ORNL has been licensed to Element3, a Texas-based company focused on extracting lithium from wastewater produced by oil and gas production.
Simulations performed on the Summit supercomputer at ORNL are cutting through that time and expense by helping researchers digitally customize the ideal alloy.

ORNL researchers modeled how hurricane cloud cover would affect solar energy generation as a storm followed 10 possible trajectories over the Caribbean and Southern U.S.

ORNL researchers are working to make EV charging more resilient by developing algorithms to deal with both internal and external triggers of charger failure. This will help charging stations remain available to traveling EV drivers, reducing range anxiety.

College intern Noah Miller is on his 3rd consecutive internship at ORNL, currently working on developing an automated pellet inspection system for Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Plutonium-238 Supply Program. Along with his success at ORNL, Miller is also focusing on becoming a mentor for kids, giving back to the place where he discovered his passion and developed his skills.
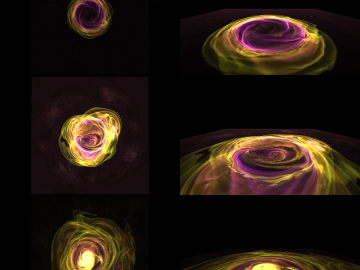
Astrophysicists at the State University of New York, Stony Brook and University of California, Berkeley, used the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility’s Summit supercomputer to compare models of X-ray bursts in 2D and 3D.




