Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Hydropower (11)
- (-) Microscopy (51)
- (-) Molten Salt (8)
- (-) Polymers (31)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (116)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (87)
- Big Data (50)
- Bioenergy (88)
- Biology (96)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (21)
- Buildings (55)
- Chemical Sciences (60)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (94)
- Composites (25)
- Computer Science (184)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (25)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (75)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (107)
- Environment (192)
- Exascale Computing (36)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Frontier (41)
- Fusion (53)
- Grid (61)
- High-Performance Computing (83)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (49)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (46)
- Materials (141)
- Materials Science (136)
- Mathematics (6)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (59)
- Net Zero (12)
- Neutron Science (130)
- Nuclear Energy (105)
- Partnerships (40)
- Physics (59)
- Quantum Computing (31)
- Quantum Science (66)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (45)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (121)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (94)
Media Contacts

Researchers set a new benchmark for future experiments making materials in space rather than for space. They discovered that many kinds of glass have similar atomic structure and arrangements and can successfully be made in space. Scientists from nine institutions in government, academia and industry participated in this 5-year study.

Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula, a scientist with joint appointments at ORNL and the University of Tennessee, has been named a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering.

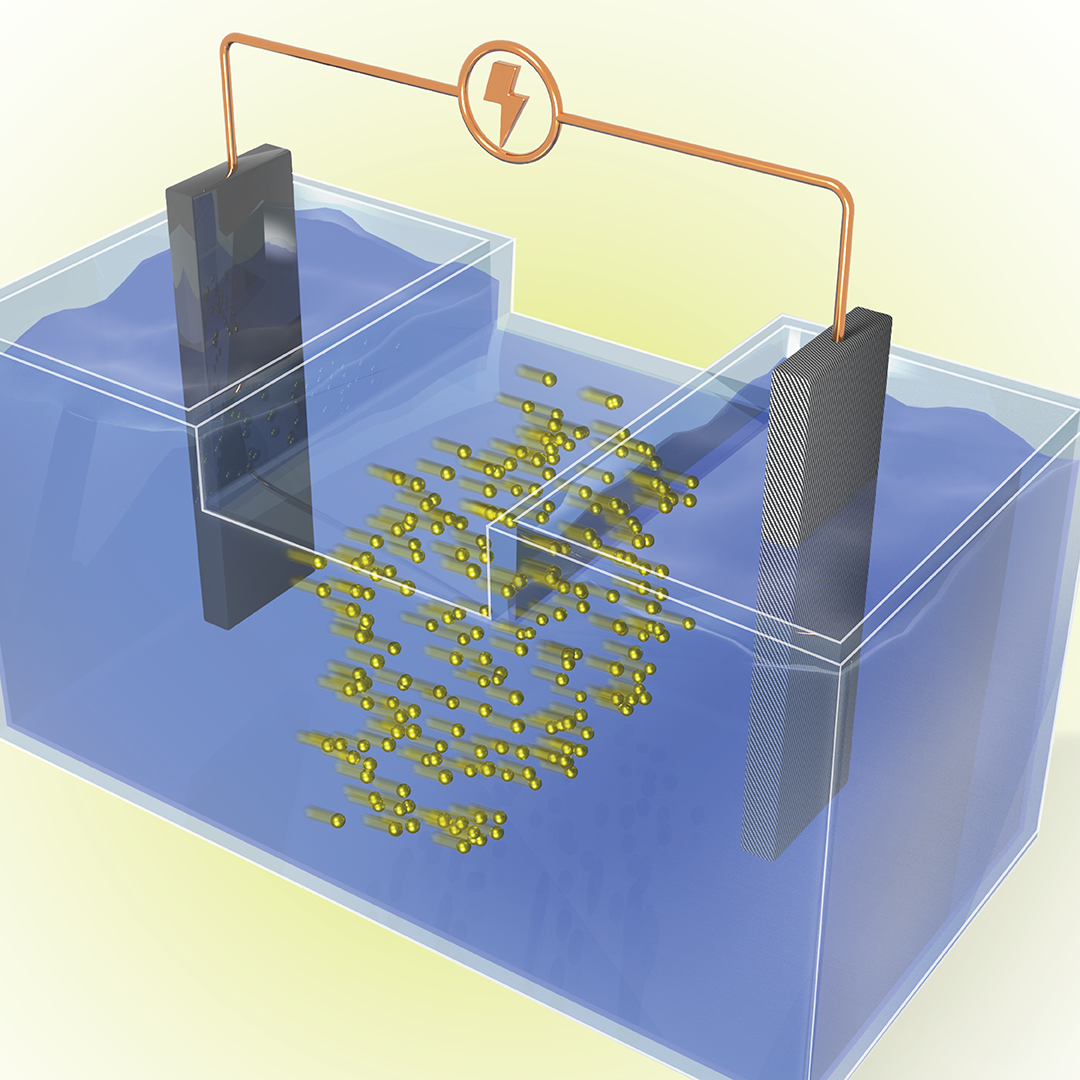
Chelsea Chen, a polymer physicist at ORNL, is studying ion transport in solid electrolytes that could help electric vehicle battery charges last longer.

New computational framework speeds discovery of fungal metabolites, key to plant health and used in drug therapies and for other uses.
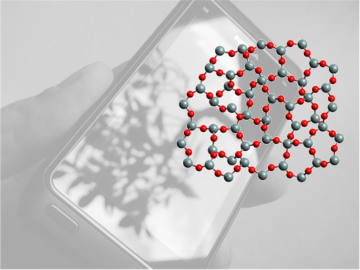
Corning uses neutron scattering to study the stability of different types of glass. Recently, researchers for the company have found that understanding the stability of the rings of atoms in glass materials can help predict the performance of glass products.
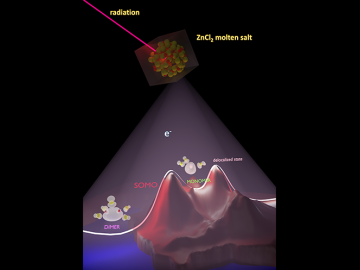
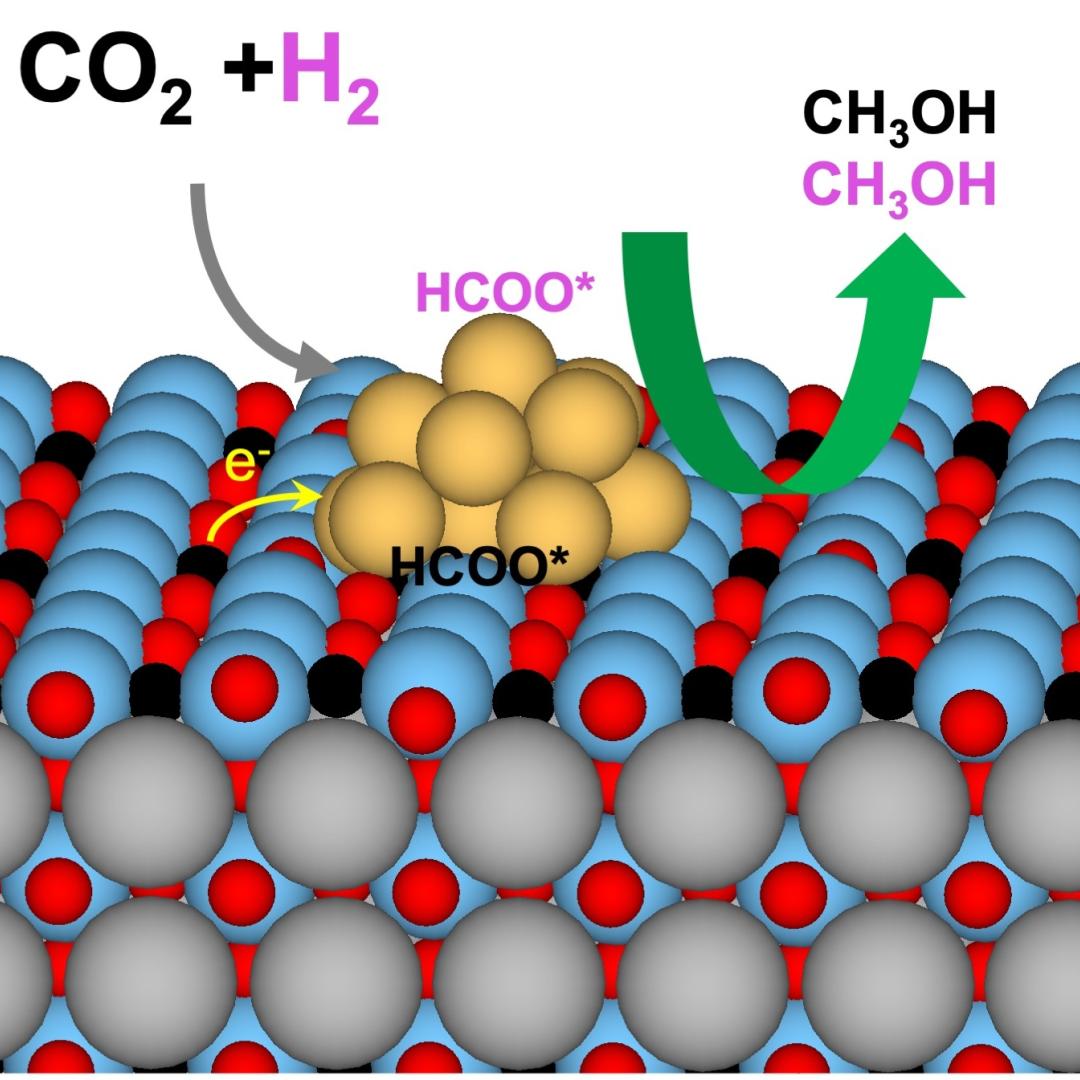
In a finding that helps elucidate how molten salts in advanced nuclear reactors might behave, scientists have shown how electrons interacting with the ions of the molten salt can form three states with different properties. Understanding these states can help predict the impact of radiation on the performance of salt-fueled reactors.

Speakers, scientific workshops, speed networking, a student poster showcase and more energized the Annual User Meeting of the Department of Energy’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, or CNMS, Aug. 7-10, near Market Square in downtown Knoxville, Tennessee.

Madhavi Martin brings a physicist’s tools and perspective to biological and environmental research at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, supporting advances in bioenergy, soil carbon storage and environmental monitoring, and even helping solve a murder mystery.

Technologies developed by researchers at ORNL have received six 2023 R&D 100 Awards.

Mirko Musa spent his childhood zigzagging his bike along the Po River. The Po, Italy’s longest river, cuts through a lush valley of grain and vegetable fields, which look like a green and gold ocean spreading out from the river’s banks.