Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (31)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Clean Energy (41)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Materials (45)
- Materials for Computing (1)
- National Security (16)
- Neutron Science (18)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (67)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (91)
- (-) Decarbonization (78)
- (-) Frontier (42)
- (-) Physics (59)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (119)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Big Data (51)
- Bioenergy (91)
- Biology (98)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (22)
- Buildings (56)
- Chemical Sciences (62)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (98)
- Composites (26)
- Computer Science (185)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (25)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (108)
- Environment (194)
- Exascale Computing (37)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Fusion (53)
- Grid (61)
- High-Performance Computing (84)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (51)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (47)
- Materials (143)
- Materials Science (138)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (60)
- Net Zero (13)
- Neutron Science (130)
- Nuclear Energy (105)
- Partnerships (41)
- Polymers (33)
- Quantum Computing (32)
- Quantum Science (67)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (45)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (124)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (95)
Media Contacts

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., March 11, 2019—An international collaboration including scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory solved a 50-year-old puzzle that explains why beta decays of atomic nuclei

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., March 4, 2019—A team of researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory Health Data Sciences Institute have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence to better match cancer patients with clinical trials.

More than 1800 years ago, Chinese astronomers puzzled over the sudden appearance of a bright “guest star” in the sky, unaware that they were witnessing the cosmic forge of a supernova, an event repeated countless times scattered across the universe.
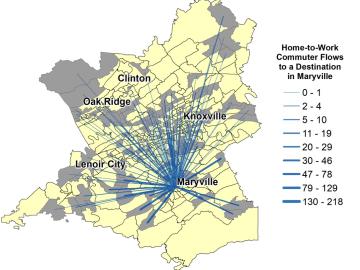
Oak Ridge National Laboratory geospatial scientists who study the movement of people are using advanced machine learning methods to better predict home-to-work commuting patterns.
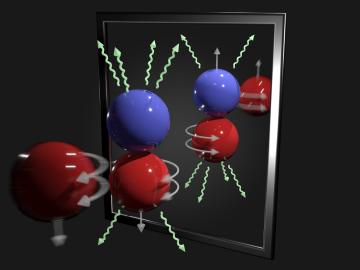
A team of scientists has for the first time measured the elusive weak interaction between protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. They had chosen the simplest nucleus consisting of one neutron and one proton for the study.

Leah Broussard, a physicist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has so much fun exploring the neutron that she alternates between calling it her “laboratory” and “playground” for understanding the universe. “The neutron is special,” she said of the sub...
Physicists turned to the “doubly magic” tin isotope Sn-132, colliding it with a target at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to assess its properties as it lost a neutron to become Sn-131.
Three researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been elected fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). Fellows of the APS are recognized for their exceptional contributions to the physics enterprise in outstanding resear...

Chang-Hong Yu of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory fell in love with running in 2008 and has since completed 38 marathons or longer-distance races. Her passion for long-distance races serves her well chasing neutrinos—electrically neutral subatomic particles th...

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are the first to successfully simulate an atomic nucleus using a quantum computer. The results, published in Physical Review Letters, demonstrate the ability of quantum systems to compute nuclear ph...




