Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Energy Frontier Research Centers (14)
- (-) Sensors and Controls (5)
- Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- Biological Systems (18)
- Biology and Environment (177)
- Biology and Soft Matter (5)
- Building Technologies (12)
- Chemical and Engineering Materials (4)
- Chemistry and Physics at Interfaces (11)
- Clean Energy (522)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (14)
- Computational Biology (6)
- Computational Chemistry (5)
- Computational Engineering (5)
- Computer Science (19)
- Data (1)
- Earth Sciences (1)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Sciences (5)
- Fossil Energy (3)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (3)
- Functional Materials for Energy (16)
- Fusion and Fission (54)
- Fusion Energy (17)
- Geographic Information Science and Technology (3)
- Isotope Development and Production (3)
- Isotopes (35)
- Materials (432)
- Materials Characterization (2)
- Materials for Computing (36)
- Materials Synthesis from Atoms to Systems (13)
- Materials Under Extremes (12)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (78)
- Neutron Data Analysis and Visualization (4)
- Neutron Science (190)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (74)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (3)
- Nuclear Systems Technology (1)
- Quantum Condensed Matter (4)
- Quantum information Science (9)
- Reactor Technology (1)
- Renewable Energy (4)
- Supercomputing (311)
- Transportation Systems (11)
News Topics
Media Contacts

A method developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to print high-fidelity, passive sensors for energy applications can reduce the cost of monitoring critical power grid assets.
Philip Bingham has two pieces of advice for researchers new to Oak Ridge National Laboratory: (1) develop a skill set that can be applied to multiple research areas, and (2) get out and meet folks across the lab. “The favorite part of my work is that I’ve done a lot of very diffe...
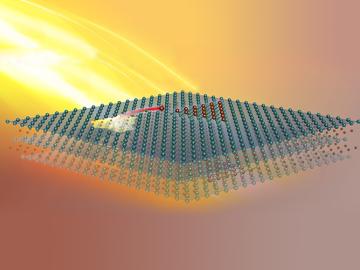
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory induced a two-dimensional material to cannibalize itself for atomic “building blocks” from which stable structures formed. The findings, reported in Nature Communications, provide insights that ...

Brixon, Inc., has exclusively licensed a multiparameter sensor technology from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The integrated platform uses various sensors that measure physical and environmental parameters and respond to standard security applications.



From the bluebird painting propped against her office wall and the deer she mentions seeing outside her office window, Linda Lewis might be mistaken for a wildlife biologist at first glance. But rather than trailing animal tracks, Lewis, a researcher at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, is more interested in marks left behind by humans.

With more than 30 patents, James Klett is no stranger to success, but perhaps the Oak Ridge National Laboratory researcher’s most noteworthy achievement didn’t start out so hot – or so it seemed at the time.

Less than 1 percent of Earth’s water is drinkable. Removing salt and other minerals from our biggest available source of water—seawater—may help satisfy a growing global population thirsty for fresh water for drinking, farming, transportation, heating, cooling and industry. But desalination is an energy-intensive process, which concerns those wanting to expand its application.

Graphene, a strong, lightweight carbon honeycombed structure that’s only one atom thick, holds great promise for energy research and development. Recently scientists with the Fluid Interface Reactions, Structures, and Transport (FIRST) Energy Frontier Research Center (EFRC), led by the US Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, revealed graphene can serve as a proton-selective permeable membrane, providing a new basis for streamlined and more efficient energy technologies such as improved fuel cells.