ORNL's Communications team works with news media seeking information about the laboratory. Media may use the resources listed below or send questions to news@ornl.gov.
31 - 40 of 1130 Results

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists identified a gene “hotspot” in the poplar tree that triggers dramatically increased root growth. The discovery supports development of better bioenergy crops and other plants that can thrive in difficult conditions while storing more carbon belowground.
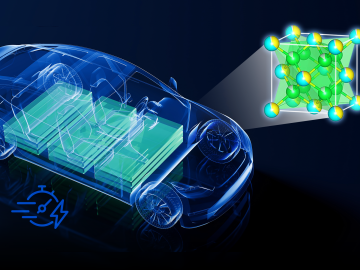
Currently, the biggest hurdle for electric vehicles, or EVs, is the development of advanced battery technology to extend driving range, safety and reliability.

An Oak Ridge National Laboratory-developed advanced manufacturing technology, AMCM, was recently licensed by Orbital Composites and enables the rapid production of composite-based components, which could accelerate the decarbonization of vehicles

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have conducted a comprehensive life cycle, cost and carbon emissions analysis on 3D-printed molds for precast concrete and determined the method is economically beneficial compared to conventional wood molds.
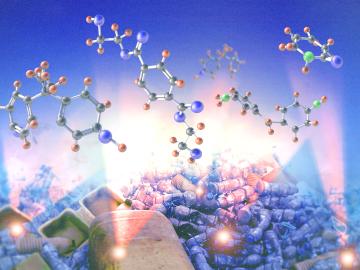
Almost 80% of plastic in the waste stream ends up in landfills or accumulates in the environment. Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have developed a technology that converts a conventionally unrecyclable mixture of plastic waste into useful chemicals, presenting a new strategy in the toolkit to combat global plastic waste.

Researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Northeastern University modeled how extreme conditions in a changing climate affect the land’s ability to absorb atmospheric carbon — a key process for mitigating human-caused emissions. They found that 88% of Earth’s regions could become carbon emitters by the end of the 21st century.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers are taking fast charging for electric vehicles, or EVs, to new extremes. A team of battery scientists recently developed a lithium-ion battery material that not only recharges 80% of its capacity in 10

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists studied hot springs on different continents and found similarities in how some microbes adapted despite their geographic diversity.

ORNL researchers have developed a training camp to help manufacturing industries reduce energy-related carbon dioxide emissions and improve cost savings.
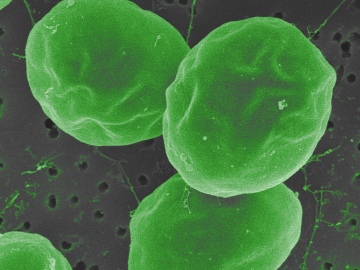
In the search for ways to fight methylmercury in global waterways, scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory discovered that some forms of phytoplankton are good at degrading the potent neurotoxin.

