Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Environment (32)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (7)
- Advanced Reactors (2)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Big Data (4)
- Bioenergy (17)
- Biology (22)
- Biomedical (6)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (9)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Clean Water (2)
- Climate Change (25)
- Composites (2)
- Computer Science (17)
- Coronavirus (3)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Decarbonization (23)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (4)
- Exascale Computing (7)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (9)
- Fusion (7)
- Grid (6)
- High-Performance Computing (14)
- Hydropower (3)
- Isotopes (6)
- ITER (1)
- Machine Learning (8)
- Materials (14)
- Materials Science (11)
- Mathematics (1)
- Mercury (1)
- Microscopy (9)
- Nanotechnology (4)
- National Security (14)
- Net Zero (5)
- Neutron Science (8)
- Nuclear Energy (7)
- Partnerships (7)
- Physics (3)
- Polymers (1)
- Quantum Computing (10)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Security (3)
- Simulation (10)
- Space Exploration (3)
- Summit (8)
- Sustainable Energy (21)
- Transportation (6)
Media Contacts

Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and six other Department of Energy national laboratories have developed a United States-based perspective for achieving net-zero carbon emissions.

The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has approved the registration and use of a renewable gasoline blendstock developed by Vertimass LLC and ORNL that can significantly reduce the emissions profile of vehicles when added to conventional fuels.

ORNL’s Erin Webb is co-leading a new Circular Bioeconomy Systems Convergent Research Initiative focused on advancing production and use of renewable carbon from Tennessee to meet societal needs.

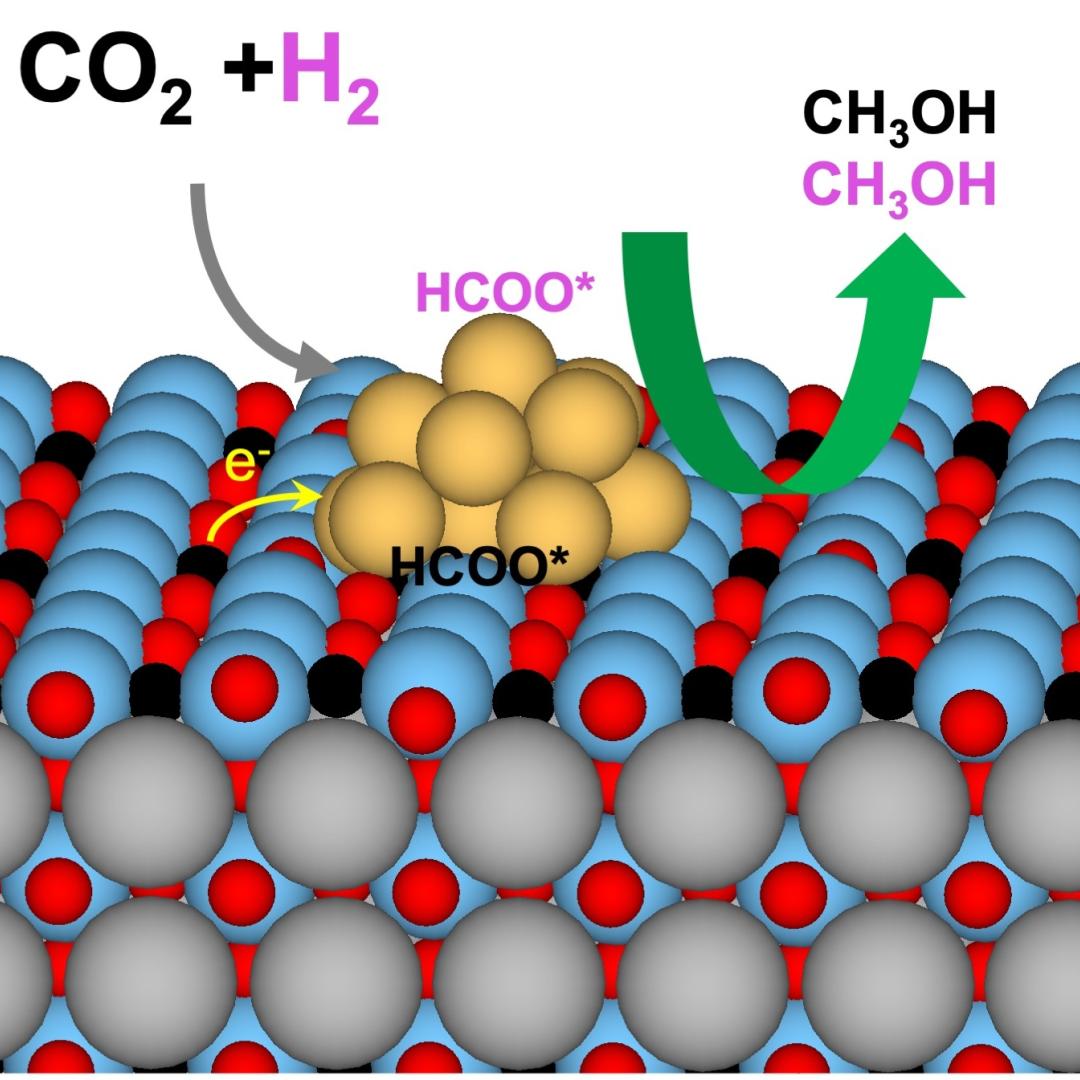
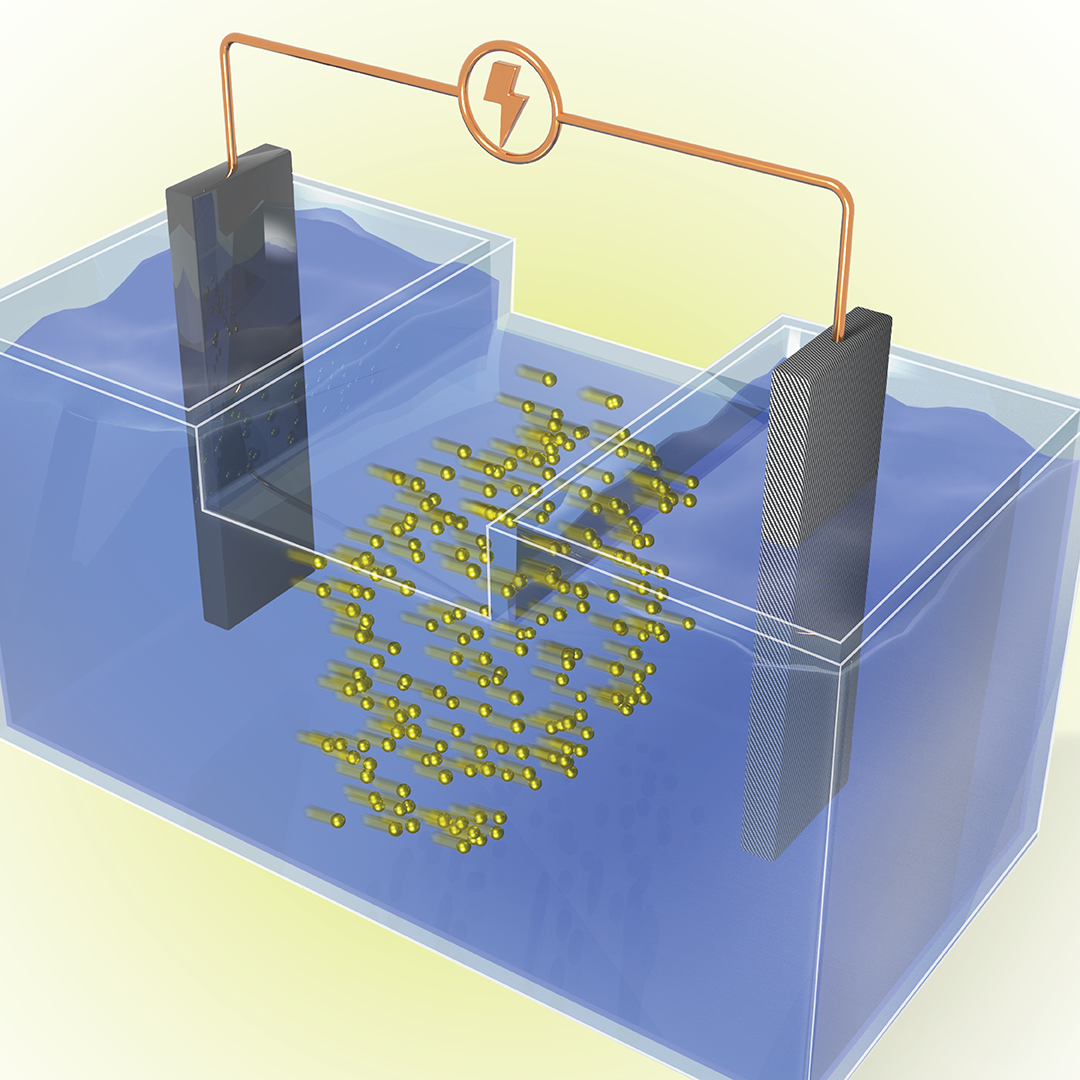
SkyNano, an Innovation Crossroads alumnus, held a ribbon-cutting for their new facility. SkyNano exemplifies using DOE resources to build a successful clean energy company, making valuable carbon nanotubes from waste CO2.

ORNL scientists and researchers attended the annual American Geophysical Union meeting and came away inspired for the year ahead in geospatial, earth and climate science.

New computational framework speeds discovery of fungal metabolites, key to plant health and used in drug therapies and for other uses.

Jack Orebaugh, a forensic anthropology major at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, has a big heart for families with missing loved ones. When someone disappears in an area of dense vegetation, search and recovery efforts can be difficult, especially when a missing person’s last location is unknown. Recognizing the agony of not knowing what happened to a family or friend, Orebaugh decided to use his internship at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to find better ways to search for lost and deceased people using cameras and drones.

David McCollum, a senior scientist at the ORNL and lead for the lab’s contributions to the Net Zero World Initiative, was one of more than 35,000 attendees in Egypt at the November 2022 Sharm El-Sheikh United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, or UNFCCC, Conference of the Parties, also known as COP27.

The interaction of elemental iron with the vast stores of carbon locked away in Arctic soils is key to how greenhouse gases are emitted during thawing and should be included in models used to predict Earth’s climate.

John “Jack” Cahill is out to illuminate previously unseen processes with new technology, advancing our understanding of how chemicals interact to influence complex systems whether it’s in the human body or in the world beneath our feet.