Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (51)
- (-) Nanotechnology (16)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (42)
- Advanced Reactors (8)
- Artificial Intelligence (48)
- Big Data (27)
- Biology (60)
- Biomedical (29)
- Biotechnology (12)
- Buildings (20)
- Chemical Sciences (26)
- Clean Water (14)
- Climate Change (50)
- Composites (8)
- Computer Science (87)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (4)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (46)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (29)
- Environment (104)
- Exascale Computing (27)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (25)
- Fusion (31)
- Grid (25)
- High-Performance Computing (45)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (27)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (22)
- Materials (43)
- Materials Science (46)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (7)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (1)
- National Security (40)
- Net Zero (8)
- Neutron Science (47)
- Nuclear Energy (55)
- Partnerships (19)
- Physics (30)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (21)
- Quantum Science (30)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (11)
- Simulation (32)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (12)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (31)
- Sustainable Energy (47)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts

In a step toward increasing the cost-effectiveness of renewable biofuels and bioproducts, scientists at ORNL discovered a microbial enzyme that degrades tough-to-break bonds in lignin, a waste product of biorefineries.

ORNL’s Zhenglong Li led a team tasked with improving the current technique for converting ethanol to C3+ olefins and demonstrated a unique composite catalyst that upends current practice and drives down costs. The research was published in ACS Catalysis.

Scientists at ORNL have discovered a single gene that simultaneously boosts plant growth and tolerance for stresses such as drought and salt, all while tackling the root cause of climate change by enabling plants to pull more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

At the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, scientists use artificial intelligence, or AI, to accelerate the discovery and development of materials for energy and information technologies.

Esther Parish is one of eight scientists from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory talking to students in nine schools across East Tennessee as part of National Environmental Education Week, or EE Week.

Through a consortium of Department of Energy national laboratories, ORNL scientists are applying their expertise to provide solutions that enable the commercialization of emission-free hydrogen fuel cell technology for heavy-duty
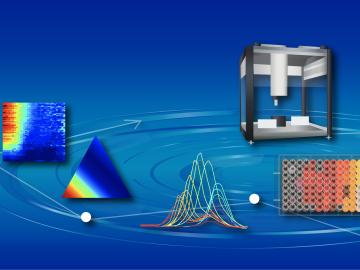
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee are automating the search for new materials to advance solar energy technologies.

As ORNL’s fuel properties technical lead for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Co-Optimization of Fuel and Engines, or Co-Optima, initiative, Jim Szybist has been on a quest for the past few years to identify the most significant indicators for predicting how a fuel will perform in engines designed for light-duty vehicles such as passenger cars and pickup trucks.

Popular wisdom holds tall, fast-growing trees are best for biomass, but new research by two U.S. Department of Energy national laboratories reveals that is only part of the equation.
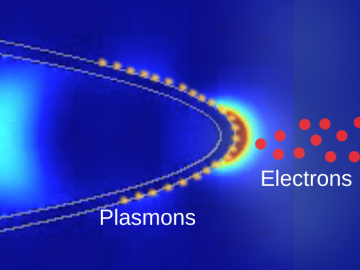
Scientists at ORNL and the University of Nebraska have developed an easier way to generate electrons for nanoscale imaging and sensing, providing a useful new tool for material science, bioimaging and fundamental quantum research.


