
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biology and Environment (44)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (7)
- Energy Science (88)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Isotopes (12)
- Materials (26)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (6)
- Neutron Science (29)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (11)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (25)
- (-) Big Data (29)
- (-) Clean Water (21)
- (-) Composites (14)
- (-) Energy Storage (45)
- (-) Environment (88)
- (-) Isotopes (18)
- (-) Neutron Science (37)
- (-) Physics (20)
- (-) Transportation (48)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (47)
- Advanced Reactors (15)
- Bioenergy (40)
- Biology (48)
- Biomedical (24)
- Biotechnology (11)
- Buildings (31)
- Chemical Sciences (22)
- Computer Science (56)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (14)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Emergency (1)
- Exascale Computing (4)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (4)
- Fusion (18)
- Grid (29)
- High-Performance Computing (23)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (4)
- Machine Learning (24)
- Materials (45)
- Materials Science (49)
- Mathematics (8)
- Mercury (7)
- Microscopy (22)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (18)
- National Security (20)
- Nuclear Energy (35)
- Partnerships (4)
- Polymers (15)
- Quantum Computing (6)
- Quantum Science (16)
- Security (8)
- Simulation (17)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (10)
Media Contacts
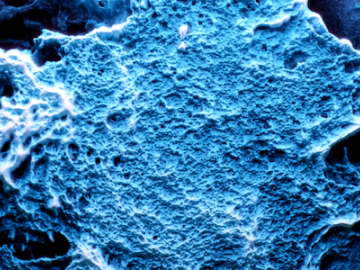
Neutron scattering techniques were used as part of a study of a novel nanoreactor material that grows crystalline hydrogen clathrates, or HCs, capable of storing hydrogen.

Matthew Craig grew up eagerly exploring the forest patches and knee-high waterfalls just beyond his backyard in central Illinois’ corn belt. Today, that natural curiosity and the expertise he’s cultivated in biogeochemistry and ecology are focused on how carbon cycles in and out of soils, a process that can have tremendous impact on the Earth’s climate.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists recently demonstrated a low-temperature, safe route to purifying molten chloride salts that minimizes their ability to corrode metals. This method could make the salts useful for storing energy generated from the sun’s heat.

Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are using ultrasounds — usually associated with medical imaging — to check the health of an operating battery. The technique uses sensors as small as a thumbnail, which could be attached to a lithium-ion battery inside a car.
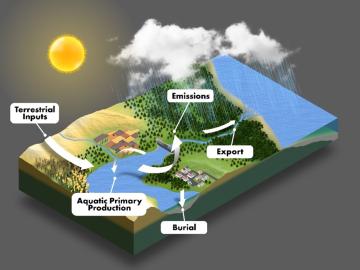
Global carbon emissions from inland waters such as lakes, rivers, streams and ponds are being undercounted by about 13% and will likely continue to rise given climate events and land use changes, ORNL scientists found.

Researchers at ORNL explored radium’s chemistry to advance cancer treatments using ionizing radiation.

When Bill Partridge started working with industry partner Cummins in 1997, he was a postdoctoral researcher specializing in applied optical diagnostics and new to Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory physicist Elizabeth “Libby” Johnson (1921-1996), one of the world’s first nuclear reactor operators, standardized the field of criticality safety with peers from ORNL and Los Alamos National Laboratory.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers are developing a first-of-its-kind artificial intelligence device for neutron scattering called Hyperspectral Computed Tomography, or HyperCT.

Chemical and environmental engineer Samarthya Bhagia is focused on achieving carbon neutrality and a circular economy by designing new plant-based materials for a range of applications from energy storage devices and sensors to environmentally friendly bioplastics.


