Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Neutron Science (35)
- (-) Supercomputing (41)
- Advanced Manufacturing (15)
- Biological Systems (2)
- Biology and Environment (32)
- Building Technologies (7)
- Chemical and Engineering Materials (1)
- Clean Energy (152)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (4)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (10)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Sciences (2)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (8)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (5)
- Materials (75)
- Materials for Computing (10)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (8)
- Neutron Data Analysis and Visualization (2)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (18)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (2)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Sensors and Controls (2)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
News Topics
- Advanced Reactors (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (2)
- Big Data (4)
- Bioenergy (1)
- Biology (1)
- Biomedical (6)
- Chemical Sciences (2)
- Climate Change (2)
- Computer Science (16)
- Coronavirus (2)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Energy Storage (3)
- Environment (5)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (1)
- High-Performance Computing (3)
- Machine Learning (1)
- Materials (4)
- Materials Science (4)
- Microscopy (1)
- Nanotechnology (2)
- Neutron Science (23)
- Nuclear Energy (2)
- Physics (1)
- Polymers (2)
- Quantum Computing (4)
- Quantum Science (4)
- Simulation (1)
- Space Exploration (2)
- Summit (6)
- Sustainable Energy (1)
- Transportation (2)
Media Contacts

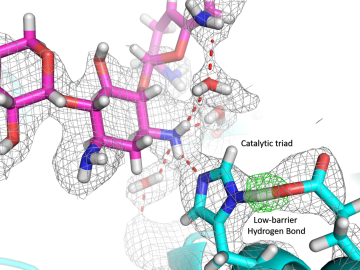
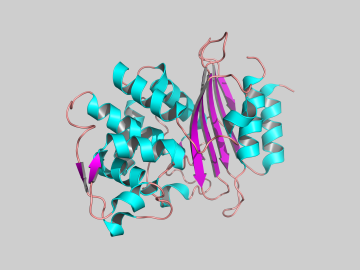
An Oak Ridge National Laboratory-led team has observed how a prolific class of antibiotics may be losing its effectiveness as certain bacteria develop drug resistance by acquiring enzymes known as aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Aminoglycosides are commonly used in antibiotics to tre...
Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have conducted a series of breakthrough experimental and computational studies that cast doubt on a 40-year-old theory describing how polymers in plastic materials behave during processing.
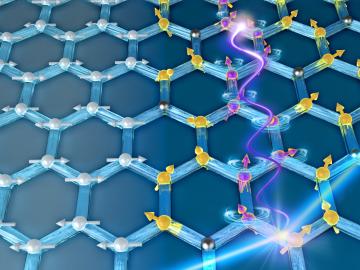
Nuclear scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are retooling existing software used to simulate radiation transport in small modular reactors, or SMRs, to run more efficiently on next-generation supercomputers. ORNL is working on various aspects of advanced SMR designs through s...