Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (10)
- Biology and Environment (65)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Clean Energy (154)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (16)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Sciences (2)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (2)
- Fusion and Fission (33)
- Fusion Energy (11)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (5)
- Materials (134)
- Materials for Computing (20)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (35)
- Neutron Science (110)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (40)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (9)
- Supercomputing (148)
News Topics
- (-) Computer Science (197)
- (-) Energy Storage (112)
- (-) Exascale Computing (42)
- (-) Frontier (45)
- (-) Machine Learning (50)
- (-) Neutron Science (135)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (111)
- (-) Physics (64)
- (-) Polymers (33)
- (-) Quantum Science (71)
- (-) Sustainable Energy (130)
- (-) Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (127)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (100)
- Big Data (60)
- Bioenergy (92)
- Biology (101)
- Biomedical (60)
- Biotechnology (24)
- Buildings (64)
- Chemical Sciences (72)
- Clean Water (31)
- Climate Change (104)
- Composites (30)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (84)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Environment (199)
- Fossil Energy (6)
- Fusion (58)
- Grid (66)
- High-Performance Computing (93)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (56)
- ITER (7)
- Materials (147)
- Materials Science (146)
- Mathematics (9)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (9)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (71)
- Net Zero (14)
- Partnerships (50)
- Quantum Computing (37)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (25)
- Simulation (51)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (59)
- Transportation (97)
Media Contacts

Office of Science to announce a new research and development opportunity led by ORNL to advance technologies and drive new capabilities for future supercomputers. This industry research program worth $23 million, called New Frontiers, will initiate partnerships with multiple companies to accelerate the R&D of critical technologies with renewed emphasis on energy efficiency for the next generation of post-exascale computing in the 2029 and beyond time frame.
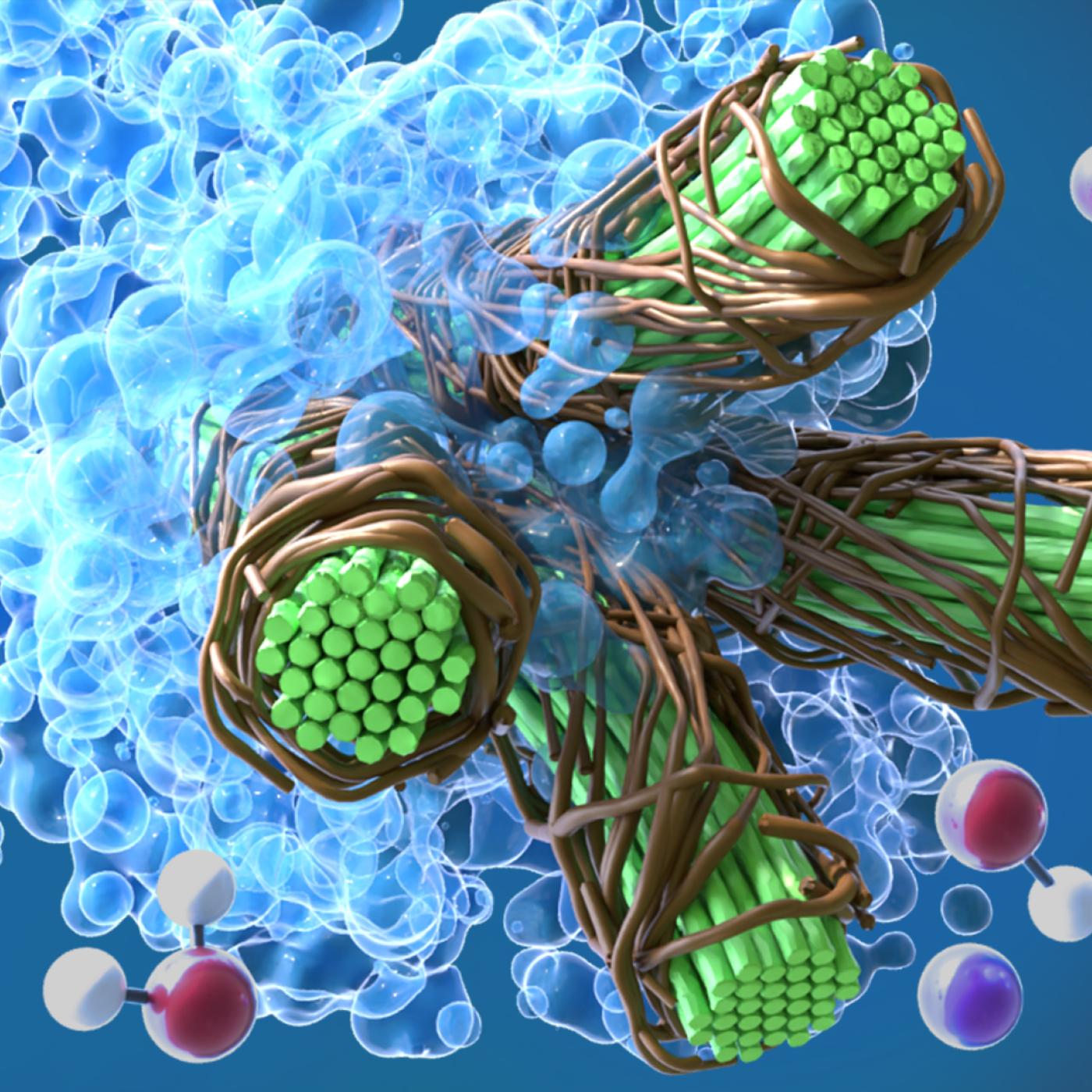
A team led by scientists at ORNL identified and demonstrated a method to process a plant-based material called nanocellulose that reduced energy needs by a whopping 21%, using simulations on the lab’s supercomputers and follow-on analysis.
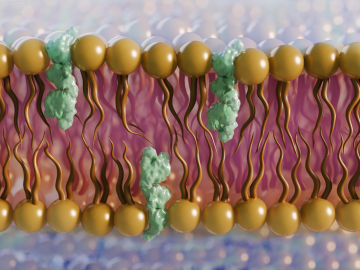
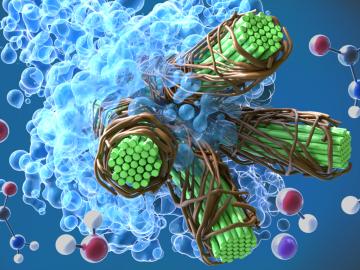
A group of scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have conducted neutron scattering research to reveal key information about fungus cell membranes that could aid in developing new antifungal treatments.

As a mechanical engineer in building envelope materials research at ORNL, Bryan Maldonado sees opportunities to apply his scientific expertise virtually everywhere he goes, from coast to coast. As an expert in understanding how complex systems operate, he’s using machine learning methods to control the process and ultimately optimize performance.

Nuclear physicists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently used Frontier, the world’s most powerful supercomputer, to calculate the magnetic properties of calcium-48’s atomic nucleus.
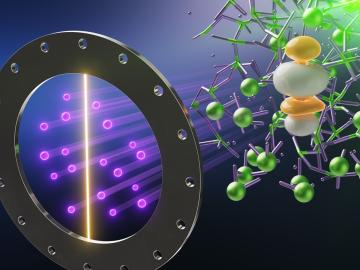
Researchers for the first time documented the specific chemistry dynamics and structure of high-temperature liquid uranium trichloride salt, a potential nuclear fuel source for next-generation reactors.

A digital construction platform in development at Oak Ridge National Laboratory is boosting the retrofitting of building envelopes and giving builders the tools to automate the process from design to installation with the assistance of a cable-driven robotic crane.

DOE commissioned a neutron imaging instrument, VENUS, at the Spallation Neutron Source in July. VENUS instrument scientists will use AI to deliver 3D models to researchers in half the time it typically takes.

A study by more than a dozen scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory examines potential strategies to integrate quantum computing with the world’s most powerful supercomputing systems in the pursuit of science.

To speed the arrival of the next-generation solid-state batteries that will power electric vehicles and other technologies, scientists led by ORNL advanced the development of flexible, durable sheets of electrolytes. They used a polymer to create a strong yet springy thin film that binds electrolytic particles and at least doubles energy storage.