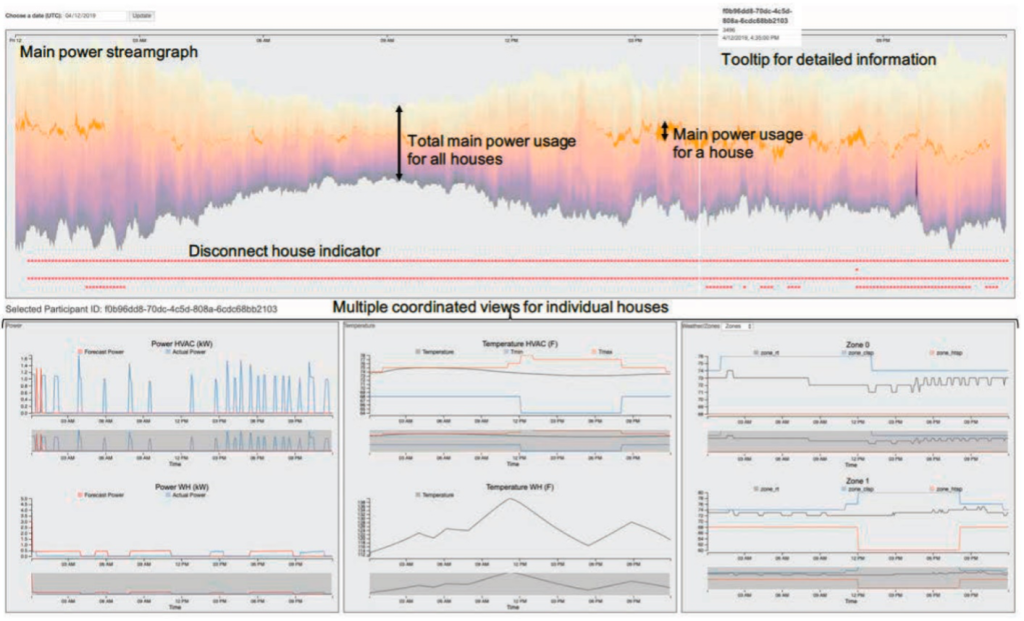
Recent advancements within smart neighborhoods where utilities are enabling automatic control of appliances such as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) and water heater (WH) systems are providing new opportunities to minimize energy costs through reduced peak load. This requires systematic collection, storage, management, and in-memory processing of large volumes of streaming data for fast performance. In this paper, we propose a multi-tier layered IoT software framework that enables effective descriptive and predictive data analysis for understanding live operation of the neighborhood, fault identification, and future opportunities for further optimization of load curves. We then demonstrate how we achieve live situational awareness of the connected neighborhood through a suite of visualization components. Finally, we discuss a few analytic dashboards that address questions such as peak load reductions obtained due to optimization, customer preference for automatic control of appliances (do they override the automatic control of HVAC?, etc.).







