
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (38)
- Clean Energy (42)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Fusion and Fission (7)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Materials (15)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (6)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (2)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Supercomputing (19)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (36)
- (-) Bioenergy (49)
- (-) Composites (6)
- (-) Frontier (23)
- (-) Microelectronics (2)
- (-) Microscopy (20)
- (-) Sustainable Energy (43)
- (-) Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Advanced Reactors (8)
- Artificial Intelligence (45)
- Big Data (21)
- Biology (57)
- Biomedical (28)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (17)
- Chemical Sciences (21)
- Clean Water (14)
- Climate Change (47)
- Computer Science (81)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (1)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (43)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (28)
- Environment (100)
- Exascale Computing (24)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Fusion (29)
- Grid (23)
- High-Performance Computing (42)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (26)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (21)
- Materials (40)
- Materials Science (43)
- Mathematics (5)
- Mercury (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (16)
- National Security (34)
- Net Zero (8)
- Neutron Science (47)
- Nuclear Energy (52)
- Partnerships (15)
- Physics (28)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (20)
- Quantum Science (30)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (10)
- Simulation (30)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (12)
- Summit (30)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts
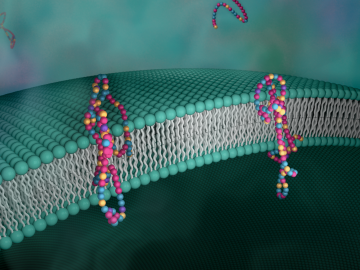
Biological membranes, such as the “walls” of most types of living cells, primarily consist of a double layer of lipids, or “lipid bilayer,” that forms the structure, and a variety of embedded and attached proteins with highly specialized functions, including proteins that rapidly and selectively transport ions and molecules in and out of the cell.
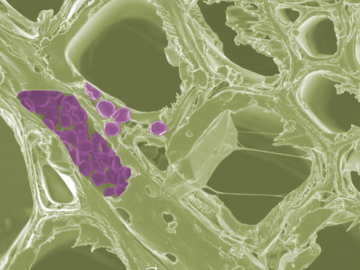
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a new method to peer deep into the nanostructure of biomaterials without damaging the sample. This novel technique can confirm structural features in starch, a carbohydrate important in biofuel production.

Peter Wang is focused on robotics and automation at the Department of Energy’s Manufacturing Demonstration Facility at ORNL, working on high-profile projects such as the MedUSA, a large-scale hybrid additive manufacturing machine.
Liam Collins was drawn to study physics to understand “hidden things” and honed his expertise in microscopy so that he could bring them to light.
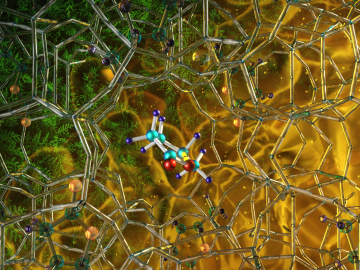
Illustration of the optimized zeolite catalyst, or NbAlS-1, which enables a highly efficient chemical reaction to create butene, a renewable source of energy, without expending high amounts of energy for the conversion. Credit: Jill Hemman, Oak Ridge National Laboratory/U.S. Dept. of Energy
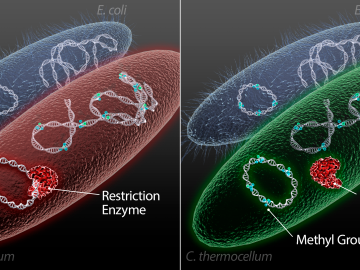
Scientists at the US Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated a method to insert genes into a variety of microorganisms that previously would not accept foreign DNA, with the goal of creating custom microbes to break down plants for bioenergy.

A modern, healthy transportation system is vital to the nation’s economic security and the American standard of living. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is engaged in a broad portfolio of scientific research for improved mobility

Early career scientist Stephanie Galanie has applied her expertise in synthetic biology to a number of challenges in academia and private industry. She’s now bringing her skills in high-throughput bio- and analytical chemistry to accelerate research on feedstock crops as a Liane B. Russell Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

In the shifting landscape of global manufacturing, American ingenuity is once again giving U.S companies an edge with radical productivity improvements as a result of advanced materials and robotic systems developed at the Department of Energy’s Manufacturing Demonstration Facility (MDF) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

When Scott Smith looks at a machine tool, he thinks not about what the powerful equipment used to shape metal can do – he’s imagining what it could do with the right added parts and strategies. As ORNL’s leader for a newly formed group, Machining and Machine Tool Research, Smith will have the opportunity to do just that.


