Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Big Data (21)
- (-) Emergency (2)
- (-) Neutron Science (46)
- (-) Software (1)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (35)
- Advanced Reactors (8)
- Artificial Intelligence (45)
- Bioenergy (49)
- Biology (57)
- Biomedical (28)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (17)
- Chemical Sciences (21)
- Clean Water (14)
- Climate Change (47)
- Composites (6)
- Computer Science (80)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (1)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (43)
- Education (1)
- Energy Storage (28)
- Environment (100)
- Exascale Computing (24)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (23)
- Fusion (28)
- Grid (23)
- High-Performance Computing (42)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (25)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (21)
- Materials (40)
- Materials Science (42)
- Mathematics (5)
- Mercury (7)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (20)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (16)
- National Security (33)
- Net Zero (8)
- Nuclear Energy (52)
- Partnerships (14)
- Physics (26)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (18)
- Quantum Science (28)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (10)
- Simulation (29)
- Space Exploration (12)
- Summit (30)
- Sustainable Energy (43)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts

Researchers set a new benchmark for future experiments making materials in space rather than for space. They discovered that many kinds of glass have similar atomic structure and arrangements and can successfully be made in space. Scientists from nine institutions in government, academia and industry participated in this 5-year study.

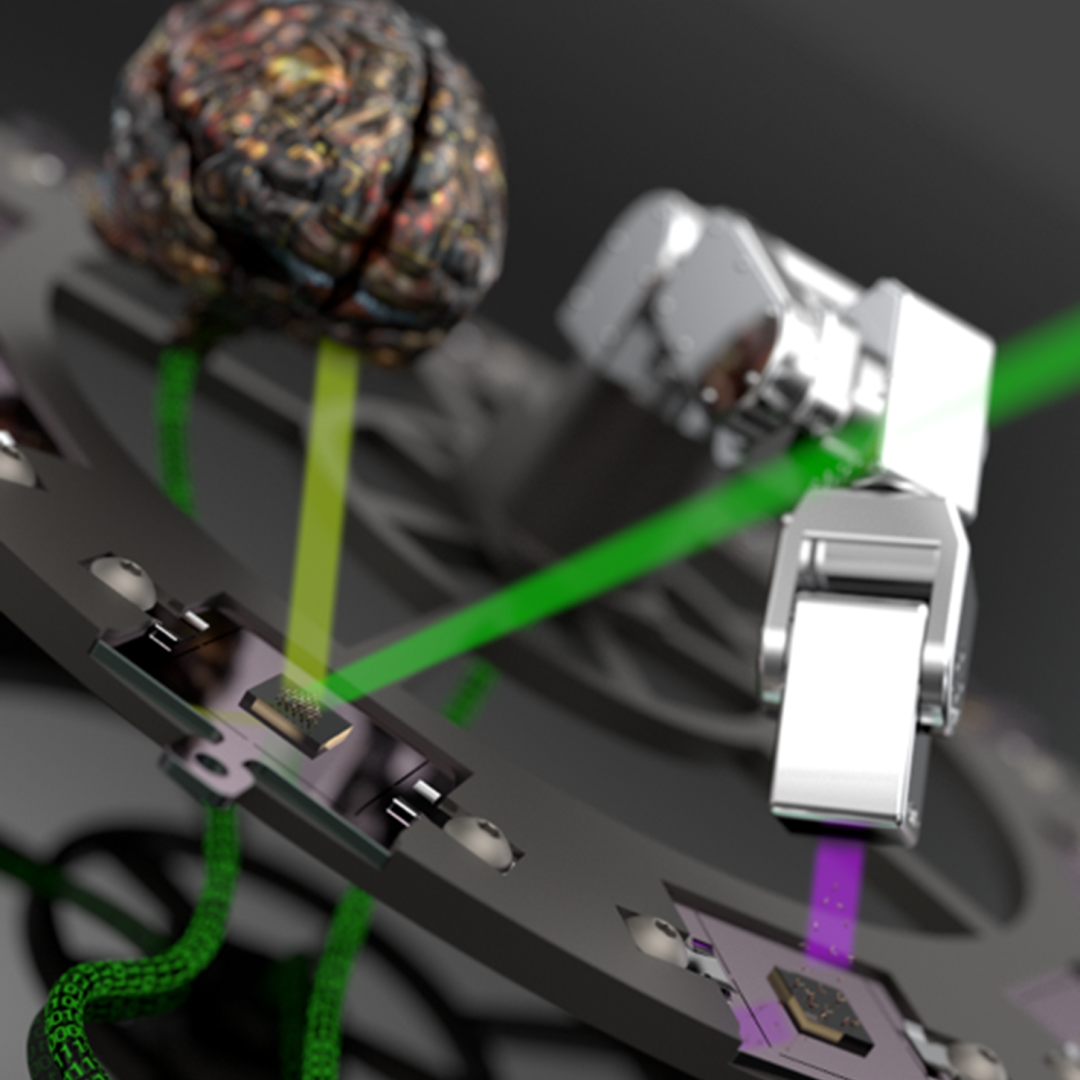
The BIO-SANS instrument, located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s High Flux Isotope Reactor, is the latest neutron scattering instrument to be retrofitted with state-of-the-art robotics and custom software. The sophisticated upgrade quadruples the number of samples the instrument can measure automatically and significantly reduces the need for human assistance.

The new section of tunnel will provide the turning and connecting point for the accelerator beamline between the existing particle accelerator at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source and the planned Second Target Station, or STS. When complete, the PPU project will increase accelerator power up to 2.8 megawatts from its current record-breaking 1.7 megawatts of beam power.

ORNL researchers modeled how hurricane cloud cover would affect solar energy generation as a storm followed 10 possible trajectories over the Caribbean and Southern U.S.
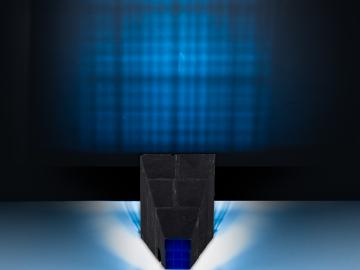
Scientists at ORNL have developed 3D-printed collimator techniques that can be used to custom design collimators that better filter out noise during different types of neutron scattering experiments
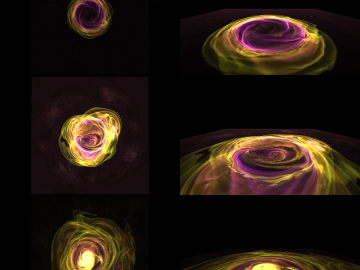
Astrophysicists at the State University of New York, Stony Brook and University of California, Berkeley, used the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility’s Summit supercomputer to compare models of X-ray bursts in 2D and 3D.

The 2023 top science achievements from HFIR and SNS feature a broad range of materials research published in high impact journals such as Nature and Advanced Materials.
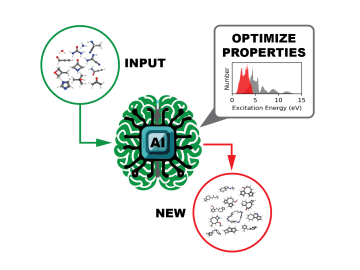
A team of computational scientists at ORNL has generated and released datasets of unprecedented scale that provide the ultraviolet visible spectral properties of over 10 million organic molecules.

Lee's paper at the August conference in Bellevue, Washington, combined weather and power outage data for three states – Texas, Michigan and Hawaii – and used a machine learning model to predict how extreme weather such as thunderstorms, floods and tornadoes would affect local power grids and to estimate the risk for outages. The paper relied on data from the National Weather Service and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Environment for Analysis of Geo-Located Energy Information, or EAGLE-I, database.

Digital twins are exactly what they sound like: virtual models of physical reality that continuously update to reflect changes in the real world.