Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Neutron Science (45)
- (-) Space Exploration (11)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- Advanced Reactors (7)
- Artificial Intelligence (40)
- Big Data (21)
- Bioenergy (48)
- Biology (56)
- Biomedical (28)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (17)
- Chemical Sciences (21)
- Clean Water (14)
- Climate Change (46)
- Composites (5)
- Computer Science (78)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (1)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (43)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (28)
- Environment (100)
- Exascale Computing (22)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (21)
- Fusion (28)
- Grid (22)
- High-Performance Computing (41)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (24)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (19)
- Materials (39)
- Materials Science (40)
- Mathematics (5)
- Mercury (7)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (19)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (16)
- National Security (32)
- Net Zero (7)
- Nuclear Energy (52)
- Partnerships (13)
- Physics (25)
- Polymers (7)
- Quantum Computing (16)
- Quantum Science (26)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (10)
- Simulation (27)
- Software (1)
- Summit (30)
- Sustainable Energy (41)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts

The BIO-SANS instrument, located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s High Flux Isotope Reactor, is the latest neutron scattering instrument to be retrofitted with state-of-the-art robotics and custom software. The sophisticated upgrade quadruples the number of samples the instrument can measure automatically and significantly reduces the need for human assistance.

The new section of tunnel will provide the turning and connecting point for the accelerator beamline between the existing particle accelerator at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source and the planned Second Target Station, or STS. When complete, the PPU project will increase accelerator power up to 2.8 megawatts from its current record-breaking 1.7 megawatts of beam power.
Scientists at ORNL have developed 3D-printed collimator techniques that can be used to custom design collimators that better filter out noise during different types of neutron scattering experiments

College intern Noah Miller is on his 3rd consecutive internship at ORNL, currently working on developing an automated pellet inspection system for Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Plutonium-238 Supply Program. Along with his success at ORNL, Miller is also focusing on becoming a mentor for kids, giving back to the place where he discovered his passion and developed his skills.
Astrophysicists at the State University of New York, Stony Brook and University of California, Berkeley, used the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility’s Summit supercomputer to compare models of X-ray bursts in 2D and 3D.

Since 2019, a team of NASA scientists and their partners have been using NASA’s FUN3D software on supercomputers located at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility to conduct computational fluid dynamics simulations of a human-scale Mars lander. The team’s ongoing research project is a first step in determining how to safely land a vehicle with humans onboard onto the surface of Mars.

The 2023 top science achievements from HFIR and SNS feature a broad range of materials research published in high impact journals such as Nature and Advanced Materials.

Nuclear engineering students from the United States Military Academy and United States Naval Academy are working with researchers at ORNL to complete design concepts for a nuclear propulsion rocket to go to space in 2027 as part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency DRACO program.
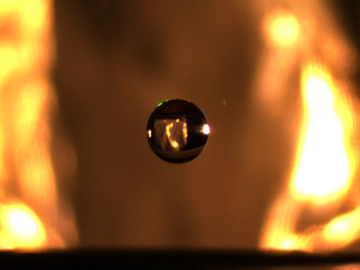
How do you get water to float in midair? With a WAND2, of course. But it’s hardly magic. In fact, it’s a scientific device used by scientists to study matter.

In response to a renewed international interest in molten salt reactors, researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a novel technique to visualize molten salt intrusion in graphite.