Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Neutron Science (16)
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (3)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Clean Energy (36)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (1)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (25)
- National Security (4)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (8)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (13)
Media Contacts
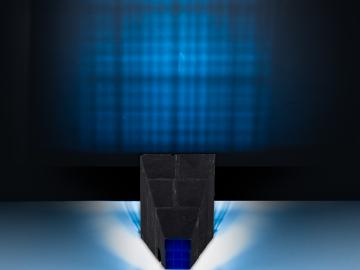
Scientists at ORNL have developed 3D-printed collimator techniques that can be used to custom design collimators that better filter out noise during different types of neutron scattering experiments
![2018-P07635 BL-6 user - Univ of Guelph-6004R_sm[2].jpg 2018-P07635 BL-6 user - Univ of Guelph-6004R_sm[2].jpg](/sites/default/files/styles/list_page_thumbnail/public/2018-P07635%20BL-6%20user%20-%20Univ%20of%20Guelph-6004R_sm%5B2%5D.jpg?itok=DUdZNt_q)
A team of scientists, led by University of Guelph professor John Dutcher, are using neutrons at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source to unlock the secrets of natural nanoparticles that could be used to improve medicines.




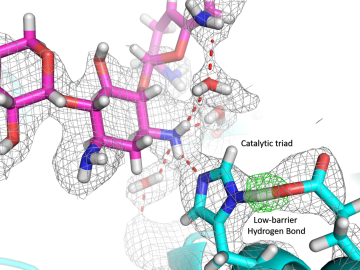
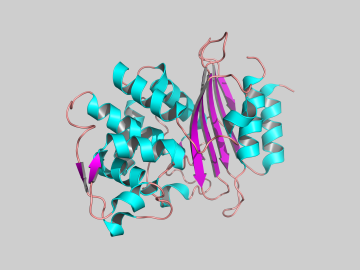
An Oak Ridge National Laboratory-led team has observed how a prolific class of antibiotics may be losing its effectiveness as certain bacteria develop drug resistance by acquiring enzymes known as aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Aminoglycosides are commonly used in antibiotics to tre...

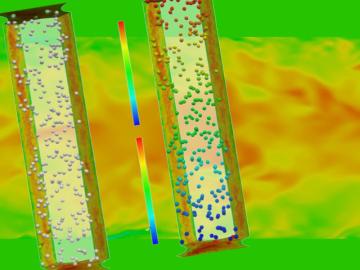
The intrinsic beauty of bubbles—those thin watery spheres filled with air or other gases—has long captured the imagination of children and adults alike. But bubbles are also a linchpin of nuclear engineering, helping to explain the natural world, predict safety issues and improve the...